| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 11484 | Draw the Shapes |
|
| 12558 | I2P(II) Chen_cpp_cheatsheet |
|
| 12789 | Weak Palindromes |
|
| 12790 | Copy a vector again |
|
Description
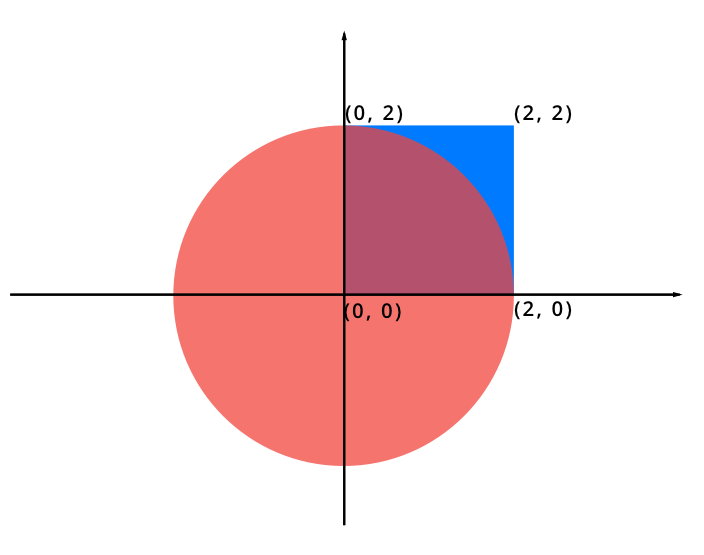
Giving basic information of some shapes, you need to draw them on the Cartesian coordinate system and calculate the total area.
PI has already defined in function.h.
Input
There are only 2 shapes in this problem :
1. R (Rectangle), followed by 4 points. Each point represent 1 vertex of the rectangle, with the format (x, y).
2. C (Circle), followed by 1 point represent the centre of the circle, and a number of its radius.
If the radius is negative, set it to 0.
e.g., the result of sample input would be like :
Output
Output the total area of all the shapes.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
11484.cppPartial Judge Header
11484.hTags
Discuss
Description
I/O optimization
If you encounter a TLE, you may try to use this optimization for C++ I/O functions:
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
And replace all std::endl with '\n'.
Do note that you must not use any of C I/O functions such as scanf, printf, fgets if you use this optimization.
<vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // sort
int main () {
std::vector<int> V;
int x;
while (std::cin >> x) {
V.push_back(x);
}
for (auto t : V) std::cout << " " << t;
std::cout << "\n";
std::sort(V.begin(), V.end());
for (auto t : V) std::cout<<" "<< t;
std::cout << "\n";
}
<queue>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
queue<string> q;
while (cin >> s) {
if (s == "Push") {
cin >> s;
q.push(s);
}
else if (s == "Pop") {
if (q.size()>0)
q.pop();
}
else if (s == "Front") {
if (q.size() == 0)
cout << "empty\n";
else
cout << q.front() << "\n";
}
}
}
<stringstream>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream> // std::stringstream
int main () {
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "Hello " << 123;
std::string s = ss.str();
std::cout << s << '\n';
}
<set>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
int main()
{
std::set<int> S = {1, 2, 3, 4};
auto search = S.find(2);
if(search != S.end()) {
std::cout << (*search) << '\n';
}
else {
std::cout << "Not found\n";
}
}
<stack>
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::stack<int> s;
s.push( 3 ); s.push( 6 );
s.push( 18 );
std::cout<<s.size()<<" elements\n";
std::cout<<"Top: "<< s.top()<< "\n";
s.pop();
std::cout<<s.size()<<" elements\n";
}
getline()
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::string name;
std::cout << "What is your name? ";
std::getline(std::cin, name);
std::cout << "Hello "<< name<< "\n";
}
<map>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <utility> // make_pair
int main()
{
std::map<std::string, int> ID;
ID.insert(std::make_pair("Tom", 123));
std::cout << ID["Tom"] << "\n";
}
<string>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str1, str2, out;
while (std::cin >> str1 >> str2) {
out.clear();
for(auto t : str1) out.push_back(t);
std::cout << out << '\n';
out += str2;
std::cout << out << '\n';
out.pop_back();
std::cout << out << '\n';
for(size_t i = 0; i < out.size(); i++)
std::cout << out[i];
std::cout << '\n';
}
}
Miscellaneous
For more standard library or C++ reference, please refer to this file and rename the downloaded file(12534.cpp) to reference.zip, then unzip it. There's a readme inside the zip.
If you have difficulty renaming file, try the following command on terminal (Windows)
move 12534.cpp reference.zip
Input
Output
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Input
Input format:
N
S_1
S_2
...
S_N
Input constraints:
1 <= N <= 1000
The length of every string will not exceed 20. Every string is distinct.
Output
S_sorted_1
S_sorted_2
...
S_sorted_N
(Print the strings in separate lines, sorted as requested in the problem description.)
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
12789.cppPartial Judge Header
12789.hTags
Discuss
Description
You must follow the rules as below:
1. do not use any static variables
2. do not use any variables which is not inside a function
3. only new, operator new, delete and operator delete are allowed to allocate or deallocate memory
4. memory usage limit: 16384 byte
You are required to implement a vector.
You have to enable C++11 in this problem. (e.g. "g++ -std=c++11 ...")
Input
There are seven functions in Vector that you have to implement, the functionality is as below:
- default constructor: initializes pointers. Do not allocate memory.
- copy constructor: copies the elements of rhs. The new capacity is rhs.size().
- copy assignment operator: copies the elements of rhs. The new capacity is max(capacity(), rhs.size()).
- erase: erases the first element that is equal to val (if it exists).
- insert: inserts a val at pos. When capacity is not enough, the new capacity is max(old capacity + 1, old capacity * 3).
- reserve: reserves storage (Increase the capacity of the container to a value that's equal to new capacity. If the new capacity is greater than the current capacity, new storage is allocated, otherwise the function does nothing.).
- destructor
For all testcases, you have to deal with reserve() and whatever is not explicitly mentioned below;
For the first testcase, you only need to deal with insert();
For the second and third, you only need insert() and erase();
For the fourth, you may only omit copy assignment;
For all, you need to do all.
Output
Complete a Vector (default constructor, copy constructor, copy assignment operator, erase, insert, reserve and destructor).