| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 12804 | Data Preprocessing |
|
| 12818 | Rolling Balls (Makeup) |
|
| 12822 | cppreference for set and map |
|
Description
Data discretization, one technic of data preprocessing, is to transform the data from complicated data into computable data, which is the critical part in a lot of application, such as Machine Learning.
In this problem, you’re asked to discretize sevaral data (name, label) (xi,yi) according to the given transform table T.
The table T consists of 2 part, before and after, which means the label y should be afteri if y is as same as beforei. Otherwise, y will become unlabeled.
After processing all data, you also have to accumulate the number of data with label = beforei for each beforei, and outputs them in the same order with table T.
For example:
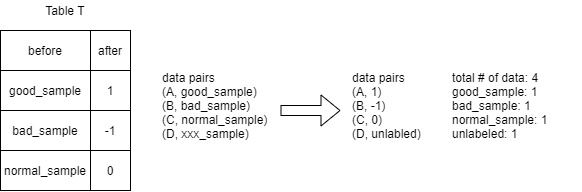
Steps:
Because the brute force method may get TLE on some testcases, TA recommonds to use 3 std::map
std::map<string, int> BA: stores (beforei, afteri) pair, in lexicological order of beforestd::map<string, int> Count: stores (beforei, Ki) denoting there’re Ki data have label = beforeistd::map<int, string> Index: store (i, beforei), which means beforei is the ith element in table T
Step 1: Read (beforei, afteri) pair, and initialize BA, Index.
Step 2: Read data (name, label), transform label by BA, and output the result.
Step 3: Accumulate the number of data with label = beforei by Count.
Step 4: Output (beforei, Ki) pair with the input order, which can be obtained by Index.
How to use std::string
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
while( cin >> s ){ // input a string until EOF
cout << "My string: " << s << endl; // string output
if( s == "XXX" ){ // built-in string comparator
cout << "s is \"XXX\"" << endl;
}
};
return 0;
}
Input
There’re multiple lines of input.
The input can be separate into 2 parts by “----------” ( ten '-' ).
The first part represents the transform table T.
Each line consists of (beforei, afteri) in table T, where beforei is a string, afteri is an integer.
The second part represents the data set.
One data (xi, yi) for one line, where xi, yi are strings.
It’s guaranteed that:
- 1 ≤ |beforei|, |xi|, |yi| ≤ 500
- beforei, xi, yi consist of lowercase alphabets.
- −10000 ≤ afteri ≤ 10000
- beforei ≠ beforej, afteri ≠ afterj for all i ≠ j
- The total number of data pairs ≤ 50000
- The size of table T ≤ 10000
Please refer to Sample Input for the precision format.
Output
First, print each data pair after discretization for one line.
Second, output the total number of data pairs.
Third, print several lines of beforei: Ki, where Ki the number of data pairs with label beforei.
Last, print the number of unlabeled data.
Notice that, the order of beforei: Ki in third part should be as same as input order.
Please refer to Sample Output for the precision format.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Tim Brown published a game “Rolling Balls”.
In this game, the player’s target is to roll balls with different colors into a moving bag as more as possible. A ball can be represented by its color (r, g, b).
Unfortunately, some unscrupulous players always want to cheat in the game.
Therefore, Tim hires you to make a cheating detection system CDSystem, which monitors and simulates the game progress to figure out any impossible data modification.
Your task is to complete a data structure called MultiSet, which can be implemented using Binary Search Tree as MultiSet_Tree.
In this problem, a MultiSet is used to represent a moving bag, into which balls with different colors can be rolled.
MultiSet
MultiSet is a data structure that supports the following operations:
- Insert(x): insert an element x into the set
- Delete(x): remove one element x from the set if there’re some x in the set
- Search(x): return the amount of x in the set
Example:
The MultiSet MS={a,b,y,y}. Search(a) = 1, Search(y) = 2, Search(x) = 0.
After Insert(x) and Delete(y), MS={a,b,x,y}. Then, Search(y) = 1, Search(x) = 1.
MultiSet_Tree
MultiSet_Tree is MultiSet implemented using Binary Search Tree, where the tree nodes store the elements and their amounts in the set. The Insert and Delete operations of MultiSet_Tree can be further explained as follows:
- Insert(x):
- Delete(x):
In this partial judge problem, you only need to complete:
MultiSet_Tree: Insert, Delete, Search- Insert: insert the Node into the MultiSet_Tree.
- Search: return the value of Node with certain key. If no such Node, return zero.
- Delete: remove 1 ball from the Tree. The Tree will be reshaped when the amount of ball is zero.
Requirements on Case 3 of Delete Operation
(Follow the requirements provided below, otherwise you will get WA !!!.)
Supposing Node x with amount == 1 is to be deleted, three possible sub-cases should be considered:
- Node x has 2 children: replace x by the Node with the largest key among the keys less than x.
- Node x has 1 child: replace x by its child Node
- Node x has no child: replace x by
NULL.
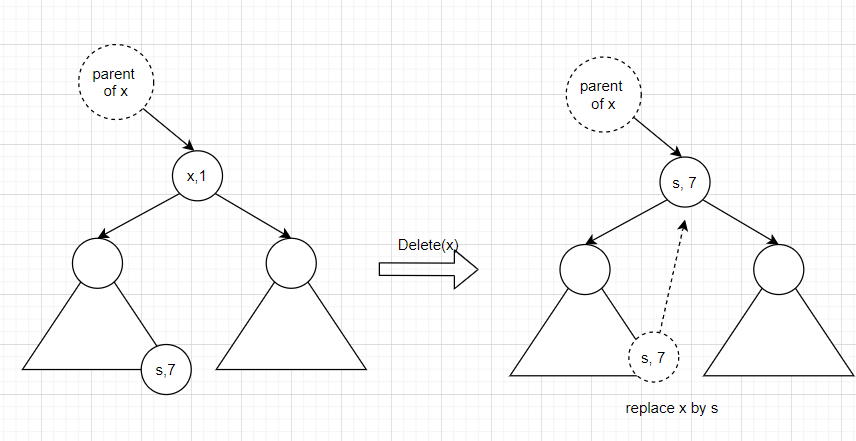
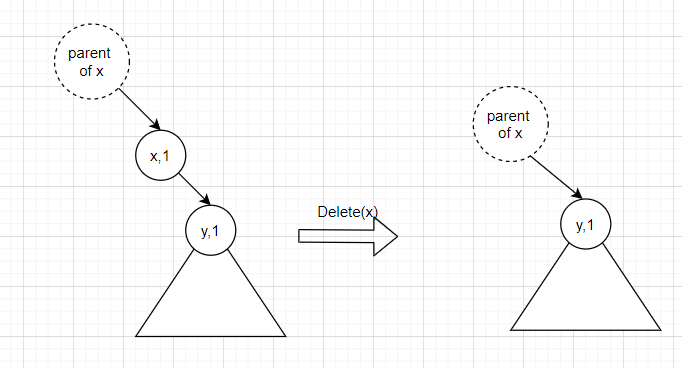
Noitce:
Please select Language C++11 when submitting code because the main.cpp use some library in C++11.
Input
The first line gives the number of test cases T.
Each case consists of one integer N and N lines of operations.
Each operation opi is with one of the following formats:
- "+ r g b": Roll a ball with color (r,g,b) into the bag.
- "- r g b": Take away a ball with color (r,g,b) from the bag. If there’s no such ball, just do nothing.
- "? r g b": Print the number of balls with color (r,g,b).
- "PrintSet": Print all nodes (key, amount, level) of
MultiSet_Treein the level-order traversal, where the key is color (r, g, b).
It’s guaranteed that:
- 1 ≤ T ≤ 200
- 0 ≤ N ≤ 5,000
- 0 ≤ r, g, b ≤ 255
- 1st testcase = sample input
- 2nd testcases only contain operations “+ r g b” , "? r g b", "PrintSet"
- 3nd testcases contain operations “+ r g b”, “? r g b”, "- r g b", "PrintSet", where "- r g b" only delete the Node which has no child.
- 4th testcases contain operations “+ r g b”, “? r g b”, "- r g b", "PrintSet", where "- r g b" have no constrain.
Output
For each test case, output one line with “Case #x:”, where x is the test case number (starting from 1).
Then print the result of each “? r g b”/“PrintSet” for one line.
Remember '\n' for the end of each line.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
12818.cppPartial Judge Header
12818.hTags
Discuss
Description
Member functions for std::set
|
(constructor)
|
constructs the set(public member function) |
|
(destructor)
|
destructs the set(public member function) |
|
operator=
|
assigns values to the container (public member function) |
|
get_allocator
|
returns the associated allocator (public member function) |
Iterators |
|
|
begincbegin
(C++11)
|
returns an iterator to the beginning (public member function) |
|
endcend
(C++11)
|
returns an iterator to the end (public member function) |
|
rbegincrbegin
(C++11)
|
returns a reverse iterator to the beginning (public member function) |
|
rendcrend
(C++11)
|
returns a reverse iterator to the end (public member function) |
Capacity |
|
|
empty
|
checks whether the container is empty (public member function) |
|
size
|
returns the number of elements (public member function) |
|
max_size
|
returns the maximum possible number of elements (public member function) |
Modifiers |
|
|
clear
|
clears the contents (public member function) |
|
insert
|
inserts elements or nodes (since C++17) (public member function) |
|
emplace
(C++11)
|
constructs element in-place (public member function) |
|
emplace_hint
(C++11)
|
constructs elements in-place using a hint (public member function) |
|
erase
|
erases elements (public member function) |
|
swap
|
swaps the contents (public member function) |
|
extract
(C++17)
|
extracts nodes from the container (public member function) |
|
merge
(C++17)
|
splices nodes from another container (public member function) |
Lookup |
|
|
count
|
returns the number of elements matching specific key (public member function) |
|
find
|
finds element with specific key (public member function) |
|
contains
(C++20)
|
checks if the container contains element with specific key (public member function) |
|
equal_range
|
returns range of elements matching a specific key (public member function) |
|
lower_bound
|
returns an iterator to the first element not less than the given key (public member function) |
|
upper_bound
|
returns an iterator to the first element greater than the given key (public member function) |
Observers |
|
|
key_comp
|
returns the function that compares keys (public member function) |
|
value_comp
|
returns the function that compares keys in objects of type value_type (public member function) |
Member functions for std::map
|
(constructor)
|
constructs the map(public member function) |
|
(destructor)
|
destructs the map(public member function) |
|
operator=
|
assigns values to the container (public member function) |
|
get_allocator
|
returns the associated allocator (public member function) |
Element access |
|
|
at
(C++11)
|
access specified element with bounds checking (public member function) |
|
operator[]
|
access or insert specified element (public member function) |
Iterators |
|
|
begincbegin
(C++11)
|
returns an iterator to the beginning (public member function) |
|
endcend
(C++11)
|
returns an iterator to the end (public member function) |
|
rbegincrbegin
(C++11)
|
returns a reverse iterator to the beginning (public member function) |
|
rendcrend
(C++11)
|
returns a reverse iterator to the end (public member function) |
Capacity |
|
|
empty
|
checks whether the container is empty (public member function) |
|
size
|
returns the number of elements (public member function) |
|
max_size
|
returns the maximum possible number of elements (public member function) |
Modifiers |
|
|
clear
|
clears the contents (public member function) |
|
insert
|
inserts elements or nodes (since C++17) (public member function) |
|
insert_or_assign
(C++17)
|
inserts an element or assigns to the current element if the key already exists (public member function) |
|
emplace
(C++11)
|
constructs element in-place (public member function) |
|
emplace_hint
(C++11)
|
constructs elements in-place using a hint (public member function) |
|
try_emplace
(C++17)
|
inserts in-place if the key does not exist, does nothing if the key exists (public member function) |
|
erase
|
erases elements (public member function) |
|
swap
|
swaps the contents (public member function) |
|
extract
(C++17)
|
extracts nodes from the container (public member function) |
|
merge
(C++17)
|
splices nodes from another container (public member function) |
Lookup |
|
|
count
|
returns the number of elements matching specific key (public member function) |
|
find
|
finds element with specific key (public member function) |
|
contains
(C++20)
|
checks if the container contains element with specific key (public member function) |
|
equal_range
|
returns range of elements matching a specific key (public member function) |
|
lower_bound
|
returns an iterator to the first element not less than the given key (public member function) |
|
upper_bound
|
returns an iterator to the first element greater than the given key (public member function) |
Observers |
|
|
key_comp
|
returns the function that compares keys (public member function) |
|
value_comp
|
returns the function that compares keys in objects of type value_type (public member function) |