| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 11371 | Polynomial multiplication using linked list |
|
| 11856 | Postfix Expression |
|
| 11933 | Vector Dot |
|
| 12306 | beat the monster |
|
| 12652 | Yoshiko And Tentacles |
|
| 12654 | Easygoing Yuri |
|
| 12692 | GY's Tree |
|
| 12817 | Social Distance |
|
| 12839 | MinMax-Heap |
|
Description
You are required to use linked list to do the multiplication of two polynomials.
Input
The input contains two lines. Each lines presents a polynomial. The format of each line is looked like : "5 4 -3 2 1 0" which means polynomial "5x4-3x2+1x0".
Each polynomial must contain a constant term. (You can use this rule to determine whether the polynomial is end.)
For example, "-2 3 1 1 0 0" should be -2x3+1x1.
(The input polynomial should be arrangement in descending power.)
Output
Output the answer. Print a space character in the begining.
For example, if the input is
5 4 -3 2 1 0 (means 5x4-3x2+1)
-2 3 1 1 0 0 (means -2x3+1x1)
the output should be
" -10 7 11 5 -5 3 1 1" (which means -10x7+11x5-5x3+x).
If the value of coefficient is 0, you don't have to print it.
(The output polynomial should be arrangement in descending power.)
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
11371.cPartial Judge Header
11371.hTags
Discuss
Description
Give a postfix expression, which has 4 operators, ‘+’ , ‘-’, '*' , '/',and positive integers. Print the result.

Notice: testcases don't include parentheses so just follow arithmetic rule.
And you don't need to consider divide 0 or some tricky rules : )
Input
The input contains exactly 1 sequences of postfix expression. It contains operators, ‘+’ ‘-’ '*' '/',and positive integers separated by a space.
The end of the input is 0.
The length of input sequence is smaller than or equal to 40
Output
The output is the result of the expression.
There is a newline symbol in the end
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Implement a Vector class that support n-dimensional vector dot product.
Your task is to complete
- const int operator[](int index) const;
- int operator*(const Vector& a);
inside the Vector class;
Remember to #include "function.h"!
Input
First line of input is an integer m, where m is the number of testcases.There are m testcases following.
A testcases consists of three lines:
- In the first line of each testcase, there are a string OP and an integer n, where OP is the operation and n is the vector size.
- In the second line of each testcase, there are n integers, representing all the elements inside the first vector, A.
- In the third line of each testcase, there are n integers, representing all the elements inside the second vector, B.
It is guaranteed that:
- 1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100
- For all the elements x in vector A and B, |x| ≤ 100
Output
For each testcase, according to its operation, output the result of A*B. There is a space after every number.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
11933.cppPartial Judge Header
11933.hTags
Discuss
Description
You are playing a game. The goal of this game is to kill the monster when you are still alive (HP > 0, HP = health point). The monster is dead if and only if its HP <= 0.
This game consists of rounds, and you go first in each round.
You have 3 options in each round:
- ATTACK. This will deduct the monster's HP. If your damage point is p, then you can deduct p monster's HP.
- HEAL. You can recover some of your HP, but it can't exceed your max HP.
- Level-up. Level-up might enhance the effect of attacking or healing, but if you are not lucky enough, sometimes it will deduct the effect of attacking and healing. Thus, choosing to level-up is not always a good choice. If you have reached max level, taking this action makes no effect.
In each round, the monster will attack you once with a fixed damage point.
You start the game with full HP and level 1. What is the minimun number of rounds you need to kill the monster?
Input
First line contains 4 numbers L, HP, MHP, MDMG.
- L = max level
- HP = your max HP
- MHP = monster's HP in the beginning of game
- MDMG = monster's damage point
The next L lines describes each level, i-th line of them describes level i. Each of them consists of two numbers, DMG and HL.
- DMG = your damage point when you use ATTACK at level i
- HL = amount of HP you can recover when you use HEAL at level i
Limits:
- L <= 15
- HP <= 300
- MHP <= 400
- MDMG <= 10000
- DMG <= 10000
- HL <= 50
Output
Print a single integer, denoting the mininum number of steps you need to kill the monster.
If you are unable to beat the monster, print -1.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Yoshiko wants to plant bananas on her farm, but it has been infected by a tentacle monster. Naturally, she wants to kill it first; now she wonders, exactly how much persticide should she buy to destroy every part of the monster.
The tentacle monster grows in the following way:
Assume that on an infinite 2D grid, a single monster spore spawns in the cell (0,0), it will at first grow upward, occupying p1 cells.

and then its growth splits into two directions: one moving +45 degrees and the other -45 degrees away from the original direction.

The monster proceeds to grow recursively: on the i-th day, extends pi cells, splits into two directions, and so on. A cell may be occupied more than once, and it will not affect the monster’s growth.
Given the number of days passed N and the extension length on day 1...N, you are to calculate how many cells have been occupied.
Note that if a cell is occupied more than once, it is still included only once in the answer.
Sample test case illustrated on a grid:

Input
Each input file contains only one testcase. On each testcase, there will be only two lines: A single integer N on the first line, followed by another line of N integers p1, p2 ... pN.
1 <= N <= 30
1 <= pi <= 5 for i = 1...N
Output
For each testcase, output a single integer: how many cells have been occupied.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Problem brought to you by NTHU Amusement Programming Club.
There is a TV show titled Easygoing Yuri, and Akarin is the protagonist in it. Over the years as more and more new characters appear, Akarin has less and less screen time. She is mortified when being told that she will have only 1 second of screen time in the new episode!
Akarin doesn’t want people to forget her, so she decides to appear in the second where she can be seen by as many as possible.
Fortunately, the audience of Easygoing Yuri is very predictable, so Akarin knows exactly the time any person starts and finishes watching. Formally, there are N people that watch Easygoing Yuri, with the i-th person watching from some integer second li until some other integer second ri, inclusively. If Akarin appears in time t with li ≤ t ≤ ri, she will be seen by the i-th person. For simplicity, she can only choose an integer-numbered second.
Can you help Akarin find out what is the maximum number of people getting to see her, if she chooses the second t optimally?
Input
There will be only one testcase in each input file.
The first line of any testcase contains a single integer N; hence comes N lines, the i-th of which contains two integers that are the li and ri whose meaning are as described in the problem statements.
1 <= N <= 2*105
0 <= li, ri <= 109 for i=1...N
Output
Output a single integer that is the maximum number of people that Akarin can get to see her.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Problem brought to you by NTHU Amusement Programming Club.
After being kicked out of NTHU due to lack of talents in programming, GY Lin had no choice but to start living in a tree (a connected, acyclic graph). If you fail this course, you will meet the same fate.

Knowing this, his friend and tutor Shepherd comes to visit GY. Unfortunately for him, GY is not at home, but he doesn’t realized this until he has already traversed every node. During that, he discovered something interesting: when he steps onto a node, the view may change dramatically.
The tree has N nodes, and nodes are numbered distinctly from 1 to N. The view from a node u can be quantified as a single integer val(u), which can be obtained using the following algorithm:
set root := u
set val(root) := 0
set boolean array vis[i]:=false for i=1...N
call dfs(root,0)
The dfs algorithm is defined as follows:
dfs(v, lv):
set vis[v] := true
val(root) := val(root) + lv
for any neighbor w of v
if vis[w]=false:
call dfs(w,lv+1)
Shepherd is now standing on node S, so he wants you to help him calculate val(S), for he doesn't have the computer right now.
Input
There is only one testcase per input file, each describing the structure of a tree.
On the first line, there two integers N S, the number of nodes and the node that Sheep is standing on; N−1 lines follow, each containing two integers u v, meaning there is an edge between node u and v.
1 <= N <= 2*105
Output
Output a single integer that is val(S).
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Since we are now undergoing the covid-19 pandemic, the CECC(疫情指揮中心) announce that two people should keep space between themselves at a social distance at s meters.
Inside a classroom, there are n seats numbered from 1 to n in a row and there are walls on the left of the 1-st seat and on the right of the n-th seat. m students numbered from 1 to m are coming to class. The distance between to neighboring seats or walls is 1 meter. Initially there are no people on the seats.

Each student takes a seat and leaves the seat at some time and they will take the seat that is farthest from the wall and the other people. If there are multiple seats to choose from, he or she will choose the leftmost one (i.e. the seat with smallest number).
More detailed description of how a student pick a seat:
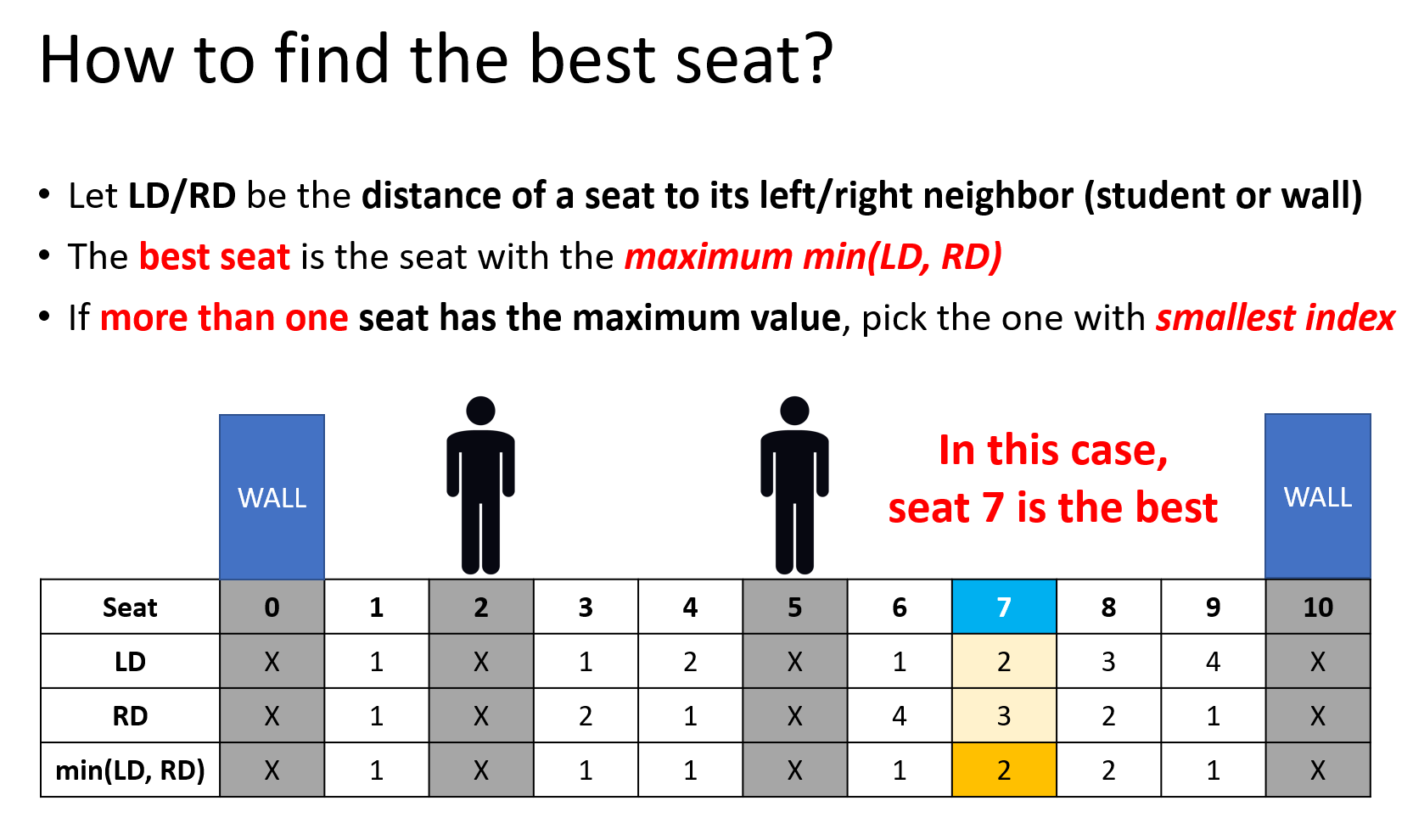
Let D be minimum distance between any two people (note that walls are not people) during the whole class. If D >= s then we say the class is safe, otherwise it is not safe.
Given the time when each student enters and leaves classroom. Your professor wants to know whether he is clockwise whether he follows the CECC's rules , so he wants you to write a program to calculate the value of D and tells him if the class is safe or not.
Explanation for sample IO
Let d be the minimum distance between any two people at a specific time.
-
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _, d = INF -
_ _ _ _ 1 _ _ _ _, d = INF -
_ 2 _ _ 1 _ _ _ _, d = 3 -
_ 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _, d = INF -
_ 2 _ _ _ 3 _ _ _, d = 4 -
_ _ _ _ _ 3 _ _ _, d = INF -
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _, d = INF
During the whole class min d = 3, therefore D = 3 < S = 5, it is not safe.
Input
The first line are three integers n m s (mentioned in problem description).
Then there are 2 x m lines, each line represents the event that one student enters or leaves the classroom. For the k-th line:
-
i xmeans that the student with number x comes in the classroom and takes a seat at time k -
o xmeans that the student with number x leaves the seat and goes out the classroom at time k
It is guaranteed that:
-
A student will never comes back to class after he or she leaves
-
When a student leaves, he or she must be in the classroom (i.e. for a student x,
i xmust appear beforeo x)
Technical Restrictions:
-
For first test case:
-
1 <= m <= n <= 10
-
1 <= s <= 10
-
-
For second test case:
-
1 <= m <= n <= 2000
-
1 <= s <= 2000
-
-
For third test case:
-
1 <= m <= 2000
-
1 <= m <= n, s <= 10^9
-
-
For fourth and fifth test case:
-
1 <= m <= 10^5
-
1 <= m <= n, s <= 10^9
-
Output
Please output D (If D is infinity, then print "INF"). Please output "YES" if it is safe and "NO" if it is not safe.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Please maintain a minmax-heap, which stores integers and is able to support following operations:
(1) PUSH k – Insert an integer k into the heap. k will fit in a 32-bit signed integer.
(2) POPMIN – Delete the minimum element from the heap. Do nothing if no elements in heap.
(3) POPMAX – Delete the maximum element from the heap. Do nothing if no elements in heap.
(4) MIN– Print the minimum element in the heap.
(5) MAX– Print the maximum element in the heap.
(5) CLEAR– Delete all elements in the heap.
Hint : std::multiset
Input
There is only one set of commands. Each command occupies a line, and the total number of commands is less than or equal to 500000. You may assume that the number of elements stored in the heap will be no more than 500000 at any time.
Output
For each “MIN/MAX” command, output a line containing the value of the element on the top of the heap. In case that the heap is empty, print ”Null” instead.