| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 10961 | Prefix expression |
|
| 11373 | Polynomial addition using linked list |
|
| 12653 | GY's Tree Pt. II |
|
| 12654 | Easygoing Yuri |
|
| 12844 | Cheat Sheet |
|
| 12851 | Multiset |
|
Description
Give a prefix expression, which only has 2 operators, ‘+’ and ‘-’,and positive integers. Print the result.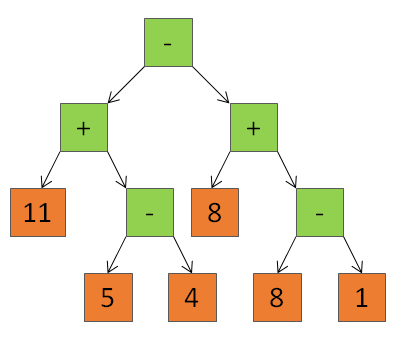
Input
The input contains a sequences of prefix expression. It contains operators, ‘+’ and ‘-’,and positive integers separated by a space. Expression is ended by 0. (0 is not the element.)
Output
The output is the result of the expression. (Without a newline symbol)
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
You are required to use linked list to do the addition of two polynomials.
Input
The input contains two lines. Each lines presents a polynomial. The format of each line is looked like : "5 4 -3 2 1 0" which means polynomial "5x4-3x2+1x0".
Each polynomial must contain a constant term. (You can use this rule to determine whether the polynomial is end.)
For example, "-2 3 1 1 0 0" should be -2x3+1x1.
(The input polynomial should be arrangement in descending power.)
Output
Output the answer. Print a space character (' ') in the begining.
For example, if the input is
5 4 -3 2 -1 1 1 0 (means 5x4-3x2-1x1+1)
-2 3 1 1 0 0 (means -2x3+1x1)
the output should be
" 5 4 -2 3 -3 2 1 0" (which means 5x4-2x3-3x2+1).
If the value of coefficient is 0, you don't have to print it.
(The output polynomial should be arrangement in descending power.)
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
11373.cPartial Judge Header
11373.hTags
Discuss
Description
Problem brought to you by NTHU Amusement Programming Club.
After being kicked out of NTHU due to lack of talents in programming, GY Lin had no choice but to start living in a tree (a connected, acyclic graph). If you fail this course, you will meet the same fate.

Knowing this, his friend and tutor Shepherd comes to visit GY. Unfortunately for him, GY is not at home, but he doesn’t realized this until he has already traversed every node. During that, he discovered something interesting: when he steps onto a node, the view may change dramatically.
The tree has N nodes, and nodes are numbered distinctly from 1 to N. The view from a node u can be quantified as a single integer val(u), which can be obtained using the following algorithm:
set root := u
set val(root) := 0
set boolean array vis[i]:=false for i=1...N
call dfs(root,0)
The dfs algorithm is defined as follows:
dfs(v, lv):
set vis[v] := true
val(root) := val(root) + lv
for any neighbor w of v
if vis[w]=false:
call dfs(w,lv+1)
Now that Shepherd has already traversed the whole tree, he wonders what is the sum of view of every node.
Input
There is only one testcase per input file, each describing the structure of a tree.
On the first line, there is a single integer N, which is the number of nodes; N−1 lines follow, each containing two integers u v, meaning there is an edge between node u and v.
1 <= N <= 2*105
Output
Output a single integer that is the sum of val(u) for u=1...N.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Problem brought to you by NTHU Amusement Programming Club.
There is a TV show titled Easygoing Yuri, and Akarin is the protagonist in it. Over the years as more and more new characters appear, Akarin has less and less screen time. She is mortified when being told that she will have only 1 second of screen time in the new episode!
Akarin doesn’t want people to forget her, so she decides to appear in the second where she can be seen by as many as possible.
Fortunately, the audience of Easygoing Yuri is very predictable, so Akarin knows exactly the time any person starts and finishes watching. Formally, there are N people that watch Easygoing Yuri, with the i-th person watching from some integer second li until some other integer second ri, inclusively. If Akarin appears in time t with li ≤ t ≤ ri, she will be seen by the i-th person. For simplicity, she can only choose an integer-numbered second.
Can you help Akarin find out what is the maximum number of people getting to see her, if she chooses the second t optimally?
Input
There will be only one testcase in each input file.
The first line of any testcase contains a single integer N; hence comes N lines, the i-th of which contains two integers that are the li and ri whose meaning are as described in the problem statements.
1 <= N <= 2*105
0 <= li, ri <= 109 for i=1...N
Output
Output a single integer that is the maximum number of people that Akarin can get to see her.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
下載後將副檔名改成zip(.cpp和.h為相同檔案,下載一個即可)
更改副檔名教學 :
打開任意資料夾 >> 點擊上方 "檢視" >> 勾選 "副檔名" >> 將.cpp或.h更改成.zip
解壓縮 >> 點進 reference 目錄 >> 點進 en 目錄 >> Main_Page.html 就可以看到完整的cpprefernce.com離線版
===================================================================================================
Download the partial judge code and change the extension to .zip. (.cpp and .h is the same file. Donwload one of them is enough.)
Open the folder with the file in it >> click "view" >> check "File name extensions" >> change .cpp or .h to .zip
Unzip the file >> click "reference" > click "en" >> open "Main_Page.html". Then you can use the offline version of cppreference.com.
Input
Output
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
12844.cppPartial Judge Header
12844.hTags
Discuss
Description
Please maintain a Multiset, which stores integers and is able to support following operations:
(1) INSERT k – Insert an integer k into the multiset. k will fit in a 32-bit signed integer.
(2) COUNT k – Print how many k in the multiset.
(3) ERASEONE k – Delete exactly one k from the multiset. Do nothing if no k in multiset.
(4) ERASEALL k – Delete all k from the multiset. Do nothing if no k in multiset.
(5) CLEAR– Delete all elements in the multiset.
Hint : you may check cheatsheet to found out the usage of multiset