| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 12301 | Uncle Huang choose Tutor(Easy version) |
|
| 12303 | Operation on Sequence |
|
| 12350 | Typing |
|
Description
Uncle Huang wants to find a tutor. He has n students to choose from.
Students are indexed 1, 2, . . . , n and standing in a circle.
Uncle Huang will count every k-th students in clock-wise.
The k-th student is going to be chosen but the student will disappear(Nobody knows why!) therefore Uncle Huang will continue his counting and start from the next student.
The last remaining student will be his tutor.
Tell Uncle Huang the index of the student who will be his tutor.
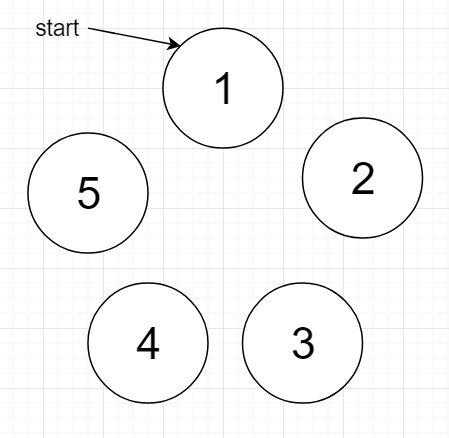
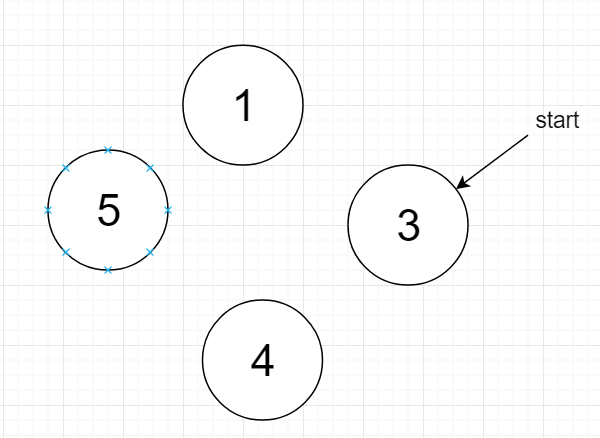
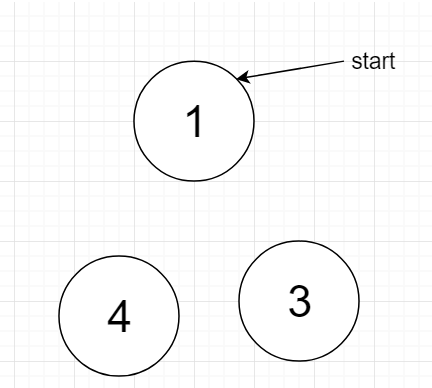
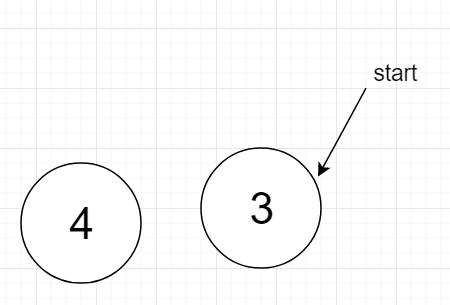
example: If n = 5, k = 7
Hint: 約瑟夫斯問題(https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%BA%A6%E7%91%9F%E5%A4%AB%E6%96%AF%E9%97%AE%E9%A2%98)
This problem is partial judge.
Note: k might be very large, if you just count k students you will get TLE. Try to count less by using mod.
Input
The input will end by EOF
Every testcase only contains two integer n(1<= n <= 1000) and k(1 <= k <= 109)
Output
For each testcase print the index of the student who last remaining.
remember to print \n at the end of every output.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
12301.cPartial Judge Header
12301.hTags
Discuss
Description
No description, literally. I'm tired.
_(:3∠」)_
-
You have a sequence
a. Initially,ahas exactly one integer. You're at the place of the1stelement. -
There are some operations below:
-
insert <val1> <val2>: insert<val2>number of elements, all with value<val1>. Insert them next to your position. -
erase <val>: erase<val>number of elements next to you. -
move <value>: Move<value>number of indexes forward. Note that<value>might be negative, which means you might move forward or backward. -
show: Start from your position, output the sequencea. Each element separated by a space. Note that there should be no space at the end but a'\n'.
-
For example: a = {2}, and execute operations below:
-
insert 3 6//a={2,3,3,3,3,3,3}, you're at the 1st position. -
insert 1 1//a={2,1,3,3,3,3,3,3}, you're at the 1st position. -
erase 2//a={2,3,3,3,3,3}, you're at the 1st position. Erase 1 and3. -
move 5//a={3,2,3,3,3,3}, you're at the 1st position. Originally was the 6th position. -
erase 3//a={3,3,3}, you're at the 1st position. Erase the first2and two3. -
show// print3 3 3. Note that there should be a'\n'at the end.
Input
The first line contains an integer x, indicates the first element in a.
The next line contains an integer n, indicates the number of operations.
There are n lines below. Each line contains exactly one operation.
1 <= n <= 3000. All numbers in a are in int range. We guaranteed that there must be at least 1 element in a, and the number of insert and erase elements won't exceed 3000.
Also, the total elements of a won't exceed 3000.
Output
Output the correct a if there's show operation.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Nderman stole a special typing machine. Because he doesn't like anybody look at him, he can only type to express himself. There're several function that this typing machine has.
(This problem is partial judge!)
void insert(Node**, char);
append one more character
charafter the cursor. Note that the cursor doesn't move after the appending.
void deletion(Node**);
delete one character after the cursor. If you reach the end of the typing, delete nothing.
void backspace(Node**);
delete one character before the cursor. If you reach the beginning of the typing, delete nothing.
void go_left(Node**, int);
move the cursor to the left for
inttimes. If you reach the beginning of the typing you should go to the end of typing and continue the moves of your cursor.
void go_right(Node**, int);
move the cursor to the right for
inttimes. If you reach the end of the typing you should go to the beginning of typing and continue the moves of your cursor.
void go_home(Node**);
move the cursor to the beginning of the typing.
void go_end(Node**);
move the cursor to the end of the typing
void show();
show all the typing.
Finish all the function except "show()"(we have done it for you).

Input
input contains several lines
First line will contain one integer n.
testcase 1 & 2:1 <= n <= 100
testcase 3 & 4:500 <= n <= 2000
Following n lines, each line contains one of the functions.
Output
If the function is show you should print all the tpying.