| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 11654 | yang_cheatsheet |
|
| 12918 | Find the maximum/minimum values |
|
| 12941 | The Game of Life |
|
| 12950 | How Many Magic Spells |
|
Description
printf() and scanf() format
printf("%d", n);
FORMAT ARGUMENT TYPE
%d, %i int decimal
%u unsigned int
%x unsigned int hexadecimal
%#x unsigned int hexadecimal with prefix 0x
%f double
%Lf long double
%c char to print a character
%s char * string (character array ended with '\0')
scanf("%d", &n);
FORMAT ARGUMENT TYPE
%d int * &n, store the input integer in n
%ld long *
%lld long long *
%u unsigned int *
%f float * read float
%lf double * read double
%Lf long double * read long double
%c char * read 3 characters %3c
%s char * read a string until whitespace
%n int * with %s, to get string length
char a[100]; int len;
scanf("%s%n", a, &len);
len will have the string length
Frequently used functions
#include <string.h>
char str[10];
scanf("%s", str);
to get the string length using strlen(str)
#include <ctype.h>
isspace(ch), islower(ch), isupper(ch), isdigit(ch)
isalpha(ch), toupper(ch), tolower(ch)
To create a 5-by-5 two-dimensional array, we need to write
int a[5][5];
It will be indexed as follows:
|
a[0][0] |
a[0][1] |
a[0][2] |
a[0][3] |
a[0][4] |
|
a[1][0] |
a[1][1] |
a[1][2] |
a[1][3] |
a[1][4] |
|
a[2][0] |
a[2][1] |
a[2][2] |
a[2][3] |
a[2][4] |
|
a[3][0] |
a[3][1] |
a[3][2] |
a[3][3] |
a[3][4] |
|
a[4][0] |
a[4][1] |
a[4][2] |
a[4][3] |
a[4][4] |
How to read the following data?
1 2 3 4 5 e
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int x;
while (scanf("%d", &x) == 1) {
printf("x=%d\n", x);
}
return 0;
}
How to read the following data?
2
L 5 2
D 5 3
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int i, n, row, col;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
while(getchar()!='\n');
scanf("%c%d%d", &ch, &row, &col);
}
return 0;
}
Using for loops to print a two-dimensional array
for(i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < col; j++) {
printf("%5d", A[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
operators:
! && || == != + - * / %
> < >= <=
How to avoid common errors and how to debug for OJ
1. Put the arrays in the 'global' area. Set their size bigger than required. Avoid using variable-length arrays (e.g. int arr[n];). Keep the array size fix (e.g., int arr[1000];).
2. After writing the code for reading input data, you may print out the data to check if your code reads them correctly. Do not proceed to write subsequent code before you confirm that.
3. If your program crashes, usually it is caused by memory related errors. Check the ranges of for-loops to see if your code attempts to read or write the elements out of the arrays' boundary.
Input
Output
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
In this problem, you are asked to implement a program which can find the maximum element M and minimum element m of a two-dimensional array. You need to print the location difference and value difference of M and m. For example, if M is at iM-th row and jM-th column and of value rM, and m is at im-th row and jm-th column and of value rm, then the location difference and value difference of the two elements are (|iM - im| + |jM - jm|) and (|rM - rm|), respectively.
Note that in a given array, no two elements will have the same value.
HINT: You can use C library function: int abs(int x) ,which returns the absolute value of int x.
Before using abs(), you may need to add the following code at first : #include <stdlib.h>
Input
The first line of the input contains two integer numbers R (2<=R<=10) and C (2<=C<=10).
Each of the next R lines contains C integers, specifying the elements of the two-dimensional array. All of the integers in the same line are separated by a space.
Output
The output contains two integers: the location difference and the value difference of the maximum and minimum elements, separated by a space.
Note that you do not need to print ‘\n’ at the end of line.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
The Game of Life is devised by the British mathematician John Horton Conway.
This Game consists of a grid of cells, each of which is in one of possible state, live or dead.
For each generation, every cell interacts with its eight neighbors in the following rules:
- Any live cell with two or three live neighbours survives.
- Any dead cell with exactly three live neighbours becomes a live cell.
- All other live cells die in the next generation. Similarly, all other dead cells stay dead.
The following 2 gifs are the examples of the Game of Life: ( Black = live, White = dead )
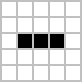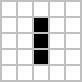

Given the initial state of n×m grid of cells.
Your task is to find the state of grid of cells after T generations.
Hint:
It's possible to access the invalid index ( arr[-1][0] ) of array when counting the neighbors.
In C, this behavior may not cause any error message.
Notice the boundary cases, and you will get AC in this problem. :)
Input
Three integers n, m, T on the first line.
The following n lines consist m numbers for each lines.
There’re si1, si2, ..., sim on the ith line, representing the initial state of grid of cells.
sij denotes the state of cell at position (i,j), 0,1 mean dead and live respectively.
It’s guaranteed that:
- 1 ≤ n, m, T ≤ 500
- sij ∈ { 0, 1 }
Output
Print the grid of cells after T generations.
Remember ‘\n’ after the end of each line.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Megumin, a talent explosion magic archwizard, spends a lot of time studying explosion magic spells. For two magic spells A and B, she found that she can combine them together to create a powerful magic spell. Moreover, if the last k characters of A matches the first k characters of B, they can be merged to obtain a more powerful spell. Refer to homework for more examples.
Soon Megumin finds magic spell A too long and wants to shorten it to some substring A'. A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string, specified with two indexes. For example, let A="yyyabcabdab", some substrings of A may be:
-
A[3...10]="abcabdab" (start from index 3 , end with index 10)
-
A[0...2]="yyy" (start from index 0 , end with index 2)
Given substring A' please tell her how many ways there are to merge A' with B.
Implementation Hints
-
Use
strlen()to retrieve length of a string with caution. Remember to#include <string.h> -
Estimating running time: recall that:
How to estimate the running time of your code?
A usual computer can run 109 basic operations (such as +, -, &, |) in 1 second. Although this depends on the judging server, this number serves as a good estimation for the running time of your code. Try to figure out how much operations your code needs to execute to finish all the computations (since not all operations in your code are basic operations, another estimate criterion is 108 operations (+, -, *, /, =, ...) in 1 second)!
-
(Maybe useless hint) Draw some examples on paper; observe them; think carefully what you can store to speed up your program.
Notes on Sample IO
Given A="yyyabcabdab", B="abcabd"
For the first substring A'=A[3…10]="abcabdab", possible ways of merging:
A' = abcabdab, B = abcabd 1) ........abcabd 2) ......abcabd
Therefore output 2
For the second substring A'=A[2…8]="yabcabd", possible ways of merging:
A' = yabcabd, B = abcabd 1) .......abcabd 2) .abcabd
Therefore output 2
For the third substring A'= A[2…7]="yabcab", possible ways of merging:
A' = yabcab, B = abcabd 1) .......abcabd 2) ....abcabd 3) .abcabd
Therefore output 3
Input
The first line is an integer T, meaning that the input has T test data. Each test data contains multiple lines.
The first line of each data are two magic spells A and B, where they only contain lower case alphabets (a-z). The second line is an integer Q. In the following Q lines, each contains a substring A' specified with two integers L and R -- the start index and end index of substring of A.
For all test cases:
-
1 <= T <= 10
-
0 <= L <= R < |A|
For test case 1-3:
-
1 <= Q, |A|, |B| <= 100
For test case 4-5:
-
1 <= Q, |A|, |B| <= 2000
For test case 6:
-
1 <= Q <= 106
-
1 <= |A|, |B| <= 2000
Output
For each substring A', output number of ways to merge A' with B in a single line. Remember to add '\n' in the end.