| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 11490 | The Cat Society |
|
| 11773 | Integer pointer array |
|
| 12568 | Reverse Linked List ver 2 |
|
| 12582 | Function Pointer Practice |
|
| 12584 | The Beauty of Distributing |
|
| 13077 | Ranking System |
|
| 13083 | Let's build a Vim editor |
|
| 13086 | Golden Ratio Overheat |
|
Description
Wild cats take care of each other in the wild. However, when winter comes, the preys are not enough to feed all the cats. Therefore, the cats dine according to the order of their occupations. The order is as follows:
1. elder
2. nursy
3. kitty
4. warrior
5. apprentice
6. medicent
7. deputy
8. leader
In the tradition of the cat society, three different cats serve as the medicent, the deputy, and the leader respectively.
As for the other cats, except that the apprentices have the dining priority of the young over the old, for the other occupations, the old have higher priority. If the occupations and the ages of two or more cats are the same, they will dine in lexicographic order according to their names.
Input
There are multiple test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers N and M, indicating the number of cats and the portions of food respectively, where 0<N,M<=10000.
The next N lines are the information of each cat, including name, occupation, and age.
The length of the names will not exceed 30 letters and will contain no spaces.
Output
Please output the cats that could eat the food in order, each name a line.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Given an integer pointer array **ptr with size N, and an integer array *array with size (N+1)*N/2. Please use malloc function to allocate memory to **ptr and *array. The *array is an ascending sequence of numbers. Each pointer in array **ptr shall point to one element of *array. And the elements pointed by the **ptr are also ascending.
For example, when n = 5, the size of **ptr will be 5, and the size of *array will be 15. The first pointer of **ptr is *ptr[0] which points to array[0], and the second pointer of **ptr is *ptr[1] which points to array[1], and the third pointer of **ptr is *ptr[2] which points to array[3], and the fourth pointer of **ptr is *ptr[3] which points to array[6].
Input
The first line is size of **ptr
The second line is offset
offset < size <10000
Output
Print each pointer of **ptr + offset
Note that you need to print a newline character ‘\n’ after each number, that is, just one number will be shown in each line of the output.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
11773.cPartial Judge Header
11773.hTags
Discuss
Description
Given several operations, push x, pop, print, reverse, create a linked list dynamicly.
- push x: Add one Node (with data = x) at the front of linked list.
- pop: Delete the Node at the front of linked list.
- reverse: reverse the current linked list
- print: output the linked list in given format.
You have to implement 3 functions:
1. void Push(Node** ptr_head,int x)
2. void Pop(Node** ptr_head)
3. void Reverse_List(Node** ptr_head)
Note: Modify the Node* head by Node** ptr_head


Input
There’re operations on several lines.
All operations are one of push x, pop, print, reverse.
It’s guaranteed that:
- Number of operations is less than 5,000,000
- Integer x is in [−1000,1000]
- The maximum length of linked list is less than 10,000.
Output
Output the linked list for every print.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
12568.cPartial Judge Header
12568.hTags
Discuss
Description
This is the practice for function pointer, you are be required to finish a task execulator using function pointer.
Given the below struct
typedef struct{
void (*func)(void *);
void *argument;
}Task;
typedef struct{
int* arr;
int lower;
int upper;
}Data;
typedef struct{
Task **tasks;
int size;
}Task_List;
and you need to implement 5 functions to pass this practice.
func1 : void job1(void* argument); // reverse
func2 : void job2(void* argument); // minus
func3 : void job3(void* argument); // double
func4 : void initTask(Task* task, void(*func)(void*),void* argument);
func5 : void executeTasks(Task_List *task_list);
For this problem, we will give you a global array and you need to modify the value in global array with different job using function pointer
Take two simple cases for example:
case 1 : when user input lower = 0, upper = 5 and method = 0 (job1) for an array A = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}
output: 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 7
case 2: when user input lower = 2, upper = 4 and method = 1 (job2) for an array A = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}
output: 1, 2, -3, -4, -5, 6, 7
case 3: when user input lower = 0, upper = 0 and method = 2 (job3) for an array A = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}
output: 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
main.c
function.h
Input
T
Mi Li Ui
...
T: the number of task (2 < T < 100)
Mi: the type of job (Mi = {0, 1, 2})
Li: the lower bound of the array (0 <= Li < 25)
Ui: the upper bound of the array (Li <= Ui < 25)
Output
Output the global array after finishing all tasks.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
12582.cPartial Judge Header
12582.hTags
Discuss
Description
Little brick is once playing a RPG game.
In this game, there are some magical reels(魔法卷軸) that can increase your skill level.
As a serious OCD patient (強迫症患者),
he can only accept that every skill he has is at the same level.
At the beginning, every skill is at level 0,
and he has N magical reels,
the ith reel can increase one of his skill by Xi levels.
LittleBrick wants to have as many skills as possible,
and he also want to use all N reels.
Tell LittleBrick what is the maximum number of skills he may have.
ouo.
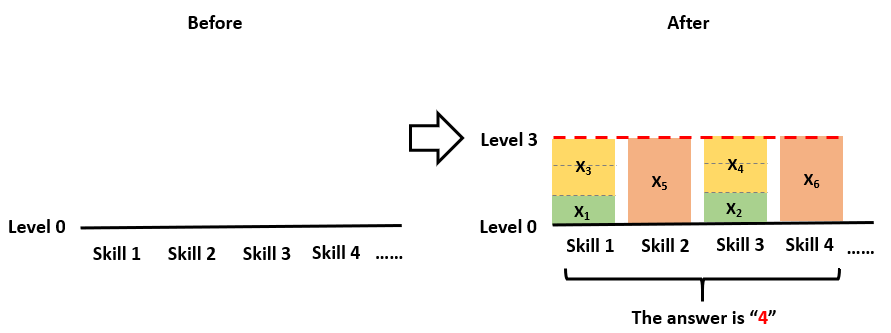
For Example 1:
6
1 1 2 2 3 3
The answer is 4, since you can make 4 skills to reach the same level 3,
by distributing the reels like (1, 2), (3), (1, 2), (3)
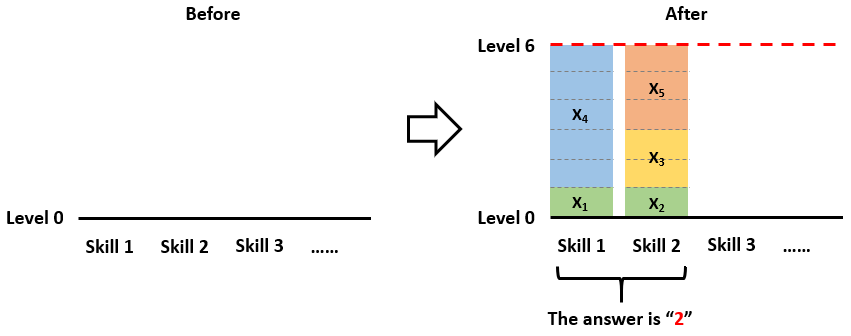
For Example 2:
5
1 1 2 5 3
The answer is 2, since you can make 2 skills to reach the same level 6,
by distributing the reels like (1, 5), (1, 2, 3)
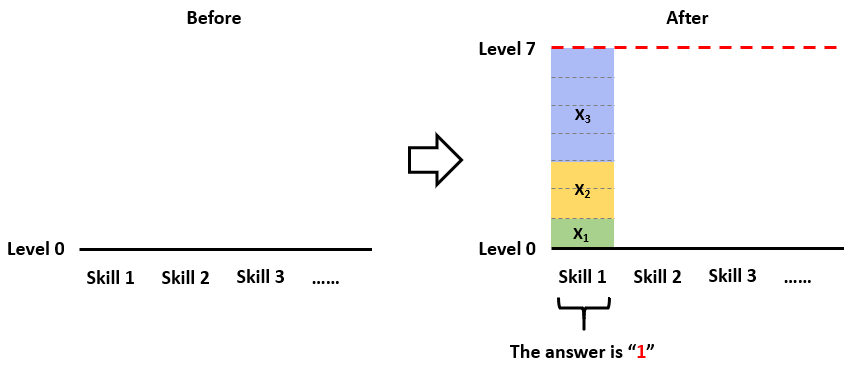
For Example 3:
3
1 2 4
The answer is 1, since you can make only 1 skill to reach the same level 7,
by distributing the reels like (1, 2, 4)
Input
The first line contains an integer T, represent the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line is an integer N,
which represents the number of reels LittleBrick has.
The next lines contain N number Xi separated by spaces,
which represents the number of levels the ith reels can increase to a single skill.
It is guarantee that:
1 <= T <= 10,
1 <= N <= 10,
1 <= Xi <= 100
Output
For each test case,
output the maximum number of skills LittleBrick can learn,
and a newline character after the answer.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Ranking system is common in everyday life.
Such as shopping site, mobile game, project contest, etc.
You have a struct of Node and a Table store Node*:
There’re 3 kinds of operation:
INSERT score, name: AddNode*with (score, name) into Table.DELETE name: Delete theNode*with name in the Table.TOP x: Returnintarray contains the indices of top x Nodes in Table.
The rank ofNode*is defined below:- The higher score, the higher rank
- For those with same score, ranking by their names in lexicological order.
Your task is to complete these 3 operations in ranking system.
Please trace the main.c, function.h for the detail interface and implementation.
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "function.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 1000
#define MAX_LEN 100
int N = 0;
Node* Table[MAX_SIZE];
int main(){
for(int i=0; i<MAX_SIZE; i++)
Table[i] = NULL;
int K;
scanf("%d", &K);
char op[10];
while( K-- ){
// printf("K: %d\n", K);
scanf("%s", op);
if( strcmp(op, "INSERT" ) == 0 ){
int score;
char name[MAX_LEN+1];
scanf("%d %s", &score, name );
Insert(Table, N, score, name );
N++;
}
else if( strcmp(op, "DELETE" ) == 0 ){
char name[MAX_LEN+1];
scanf("%s", name);
Delete(Table, N, name );
N--;
}
else if( strcmp(op, "TOP" ) == 0 ){
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
int* idxs = Top(Table, N, x);
printf("Top %d:\n", x);
for(int i=0; i<x; i++){
printf("%d %s\n", Table[idxs[i]]->score, Table[idxs[i]]->name );
}
free( idxs );
}
}
for(int i=0; i<MAX_SIZE; i++){
if( Table[i] != NULL ){
free(Table[i]->name);
free(Table[i]);
Table[i] = NULL;
}
}
return 0;
}
functin.h
// function.h
#ifndef __FUNCTION_H__
#define __FUNCTION_H__
typedef struct{
int score;
char* name;
} Node;
// Node* Table[MAX_SIZE];
// N = number of nodes in Table
void Insert( Node** Table, int N, int score, char* name );
void Delete( Node** Table, int N, char* name );
int* Top( Node** Table, int N, int x);
#endif
Input
There’s an integer K on the first line.
There’s 1 operation on the each of following K lines.
It’s guaranteed that:
- The # of elements in Table will not exceed 1000 during the process
- 1 ≤ The length of all names ≤ 100
- All names are distinct.
Output
Print the top x students in the Table for each TOP x operation.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
13077.cPartial Judge Header
13077.hTags
Discuss
Description
Vim is an editor to create or edit a text file.
There are two modes in Vim. One is the command(normal) mode and another is the insert mode.
In the command mode, user can move around the file, delete text, etc.
In the insert mode, user can insert text.
It's OK that you don't know how to exit Vim :)
The following commands are only used in command mode:
- h: move the cursor left
- l: move the cursor right (this is lowercase L, not uppercase i)
- x: delete the character at the cursor
In command mode, Vim also support a number combines with the above commands.
Let's suppose n is a number:
- nh: move the cursor left n times
- nl: move the cursor right n times
- nx: delete n characters backward from the current cursor.
To enter insert mode from command mode, the following commands are used:
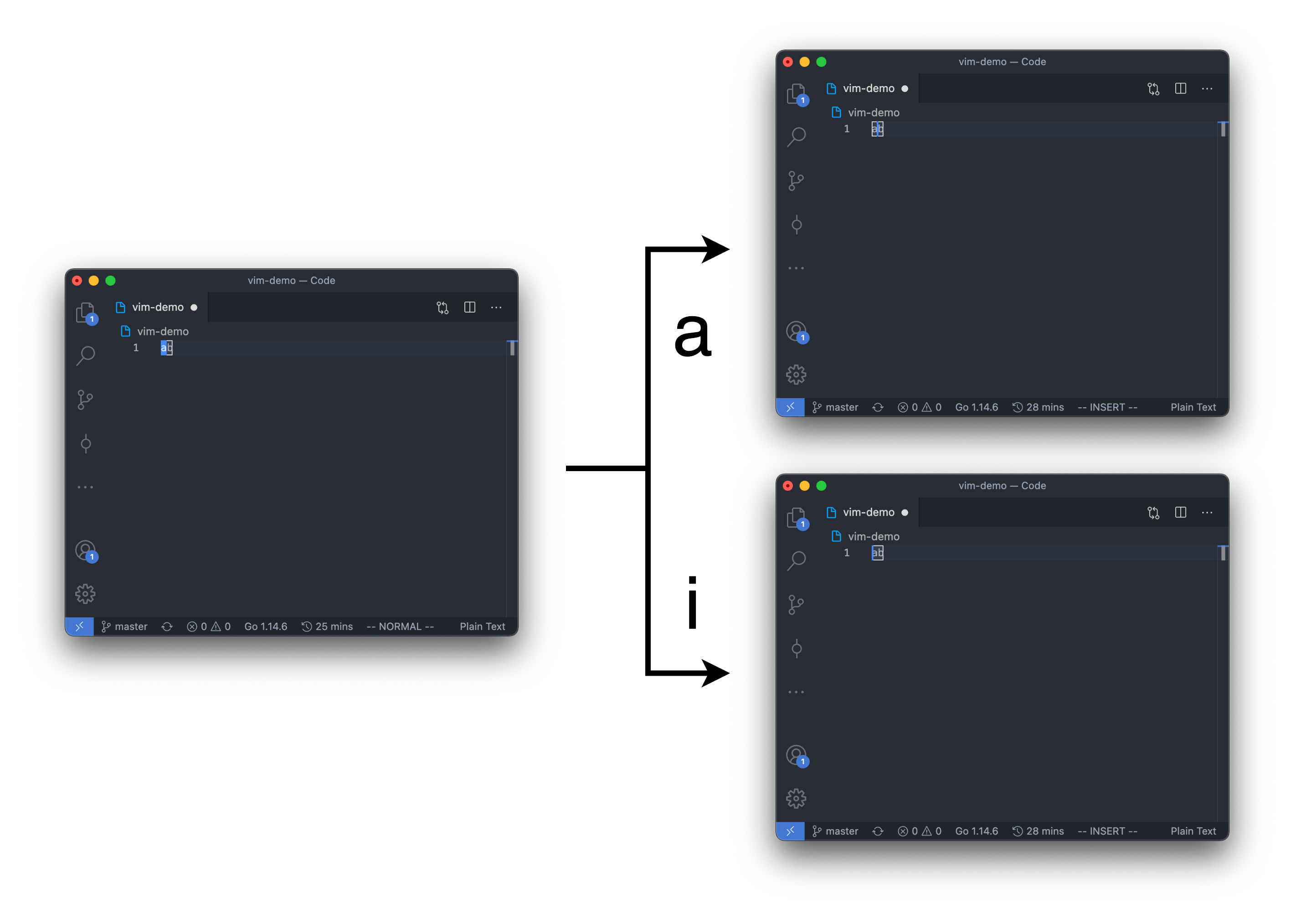
- a: enter insert mode after the current cursor
- A: enter insert mode at the end of the line
- i: enter insert mode before the current cursor
- I: enter insert mode at the beginning of the line (this is uppercase i, not lowercase L)
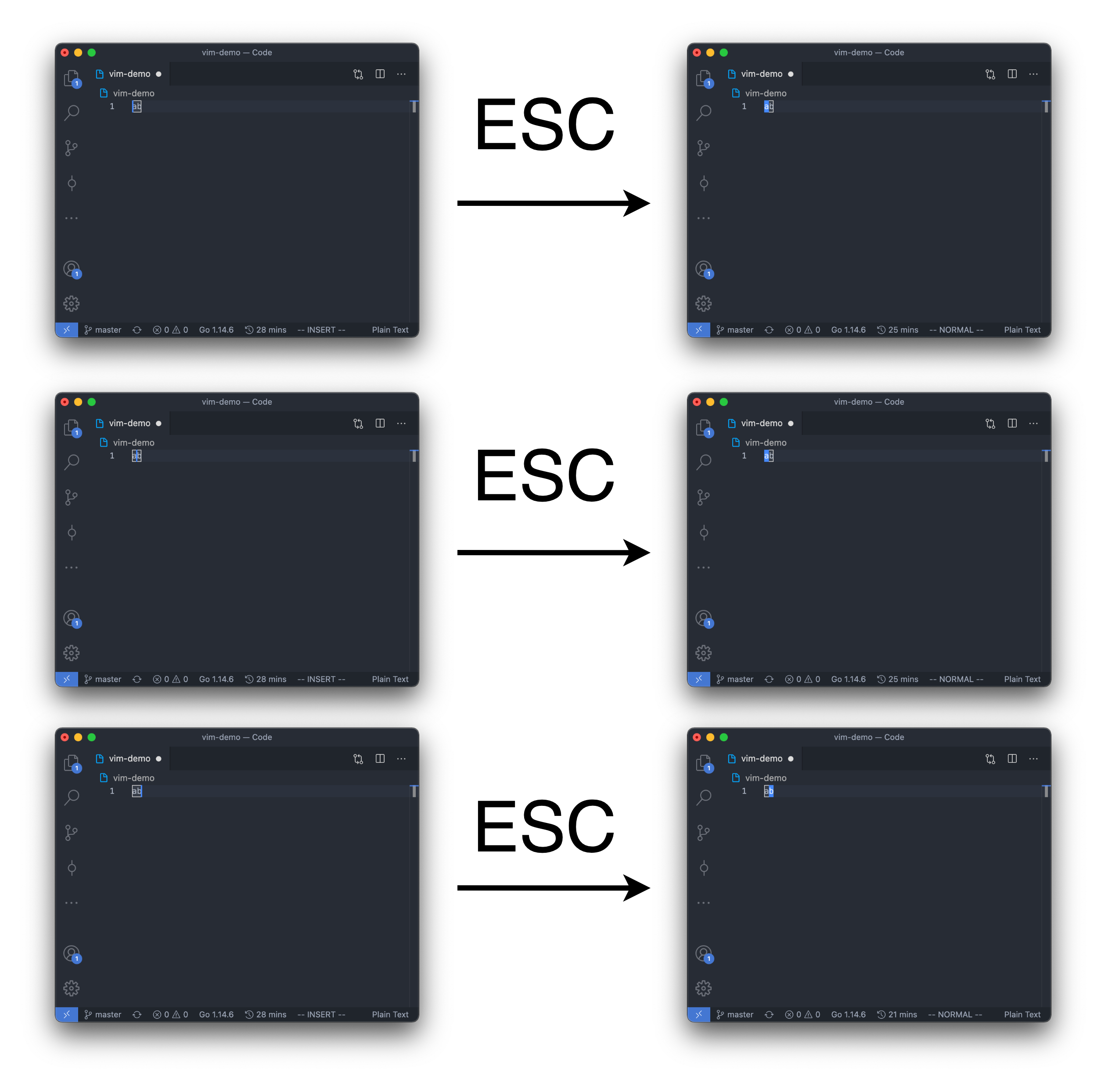
To enter command mode (from insert mode or command mode), we pressed ESC (escape) to do that.
In this problem, we used "ESC" to represents that the user entered the escape key.
At first, user is in the command mode,
and there is only 1 line in the Vim editor. (The line is empty)
Given the user input, output the text of the editor.
All test cases will end with ":wq" (without quotes) in command mode.
ouo.
Note that in command mode, the cursor can only be on the character if there is any.
So there will be 2 possible positions for the cursor in command mode if the text in the editor is "ab".
And of course, if there is no text in the editor, the cursor can only be at the beginning of the line.
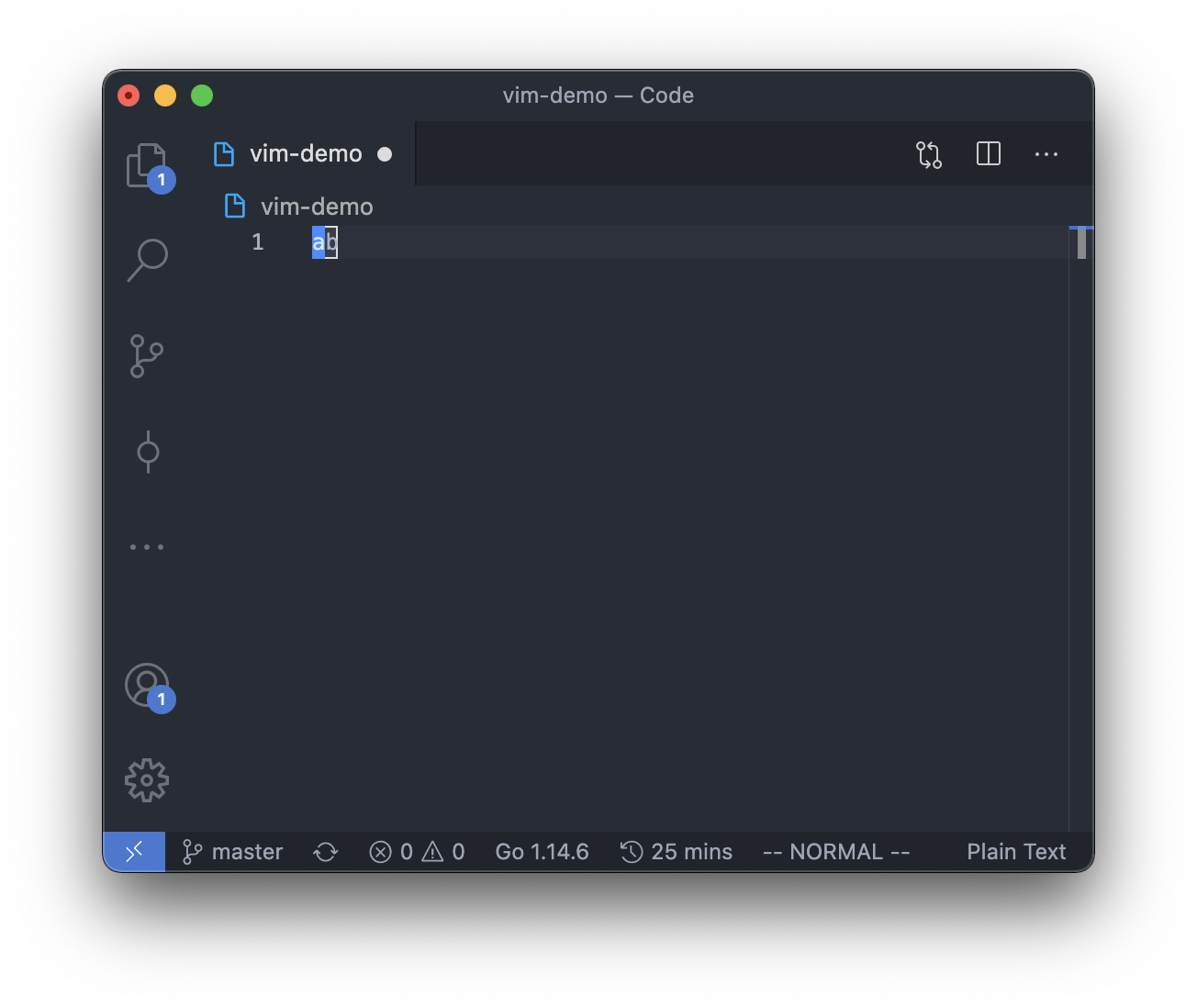
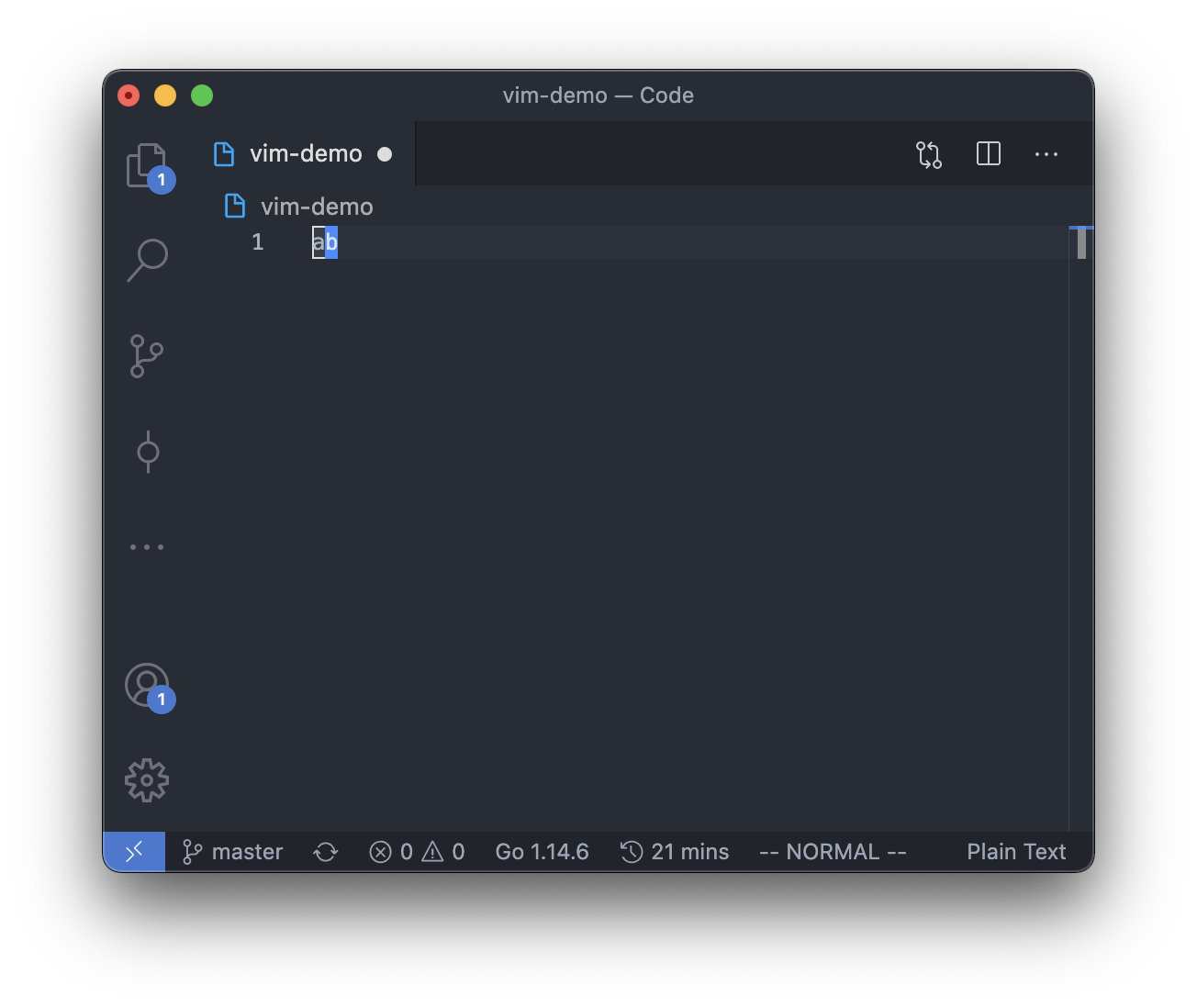
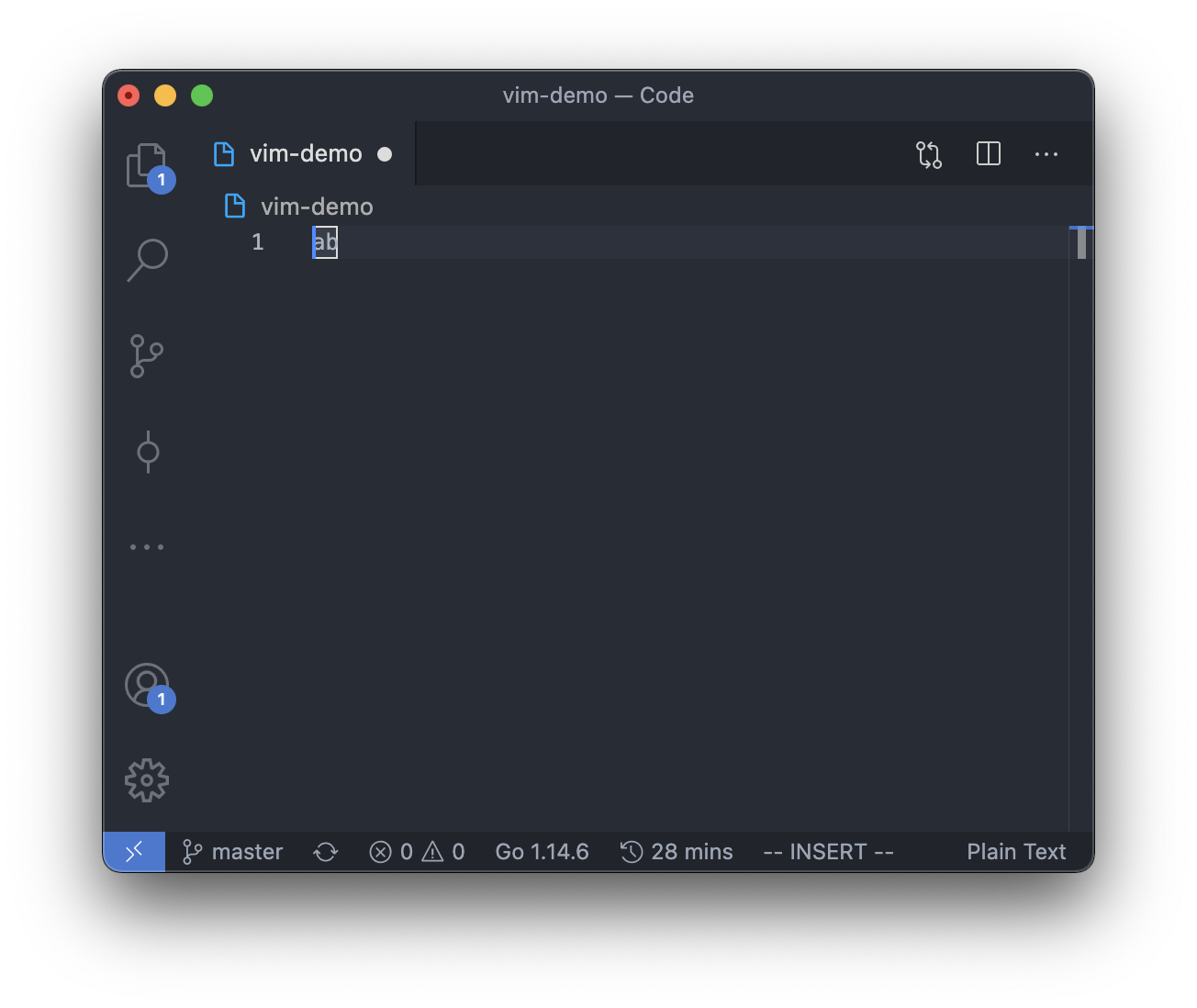
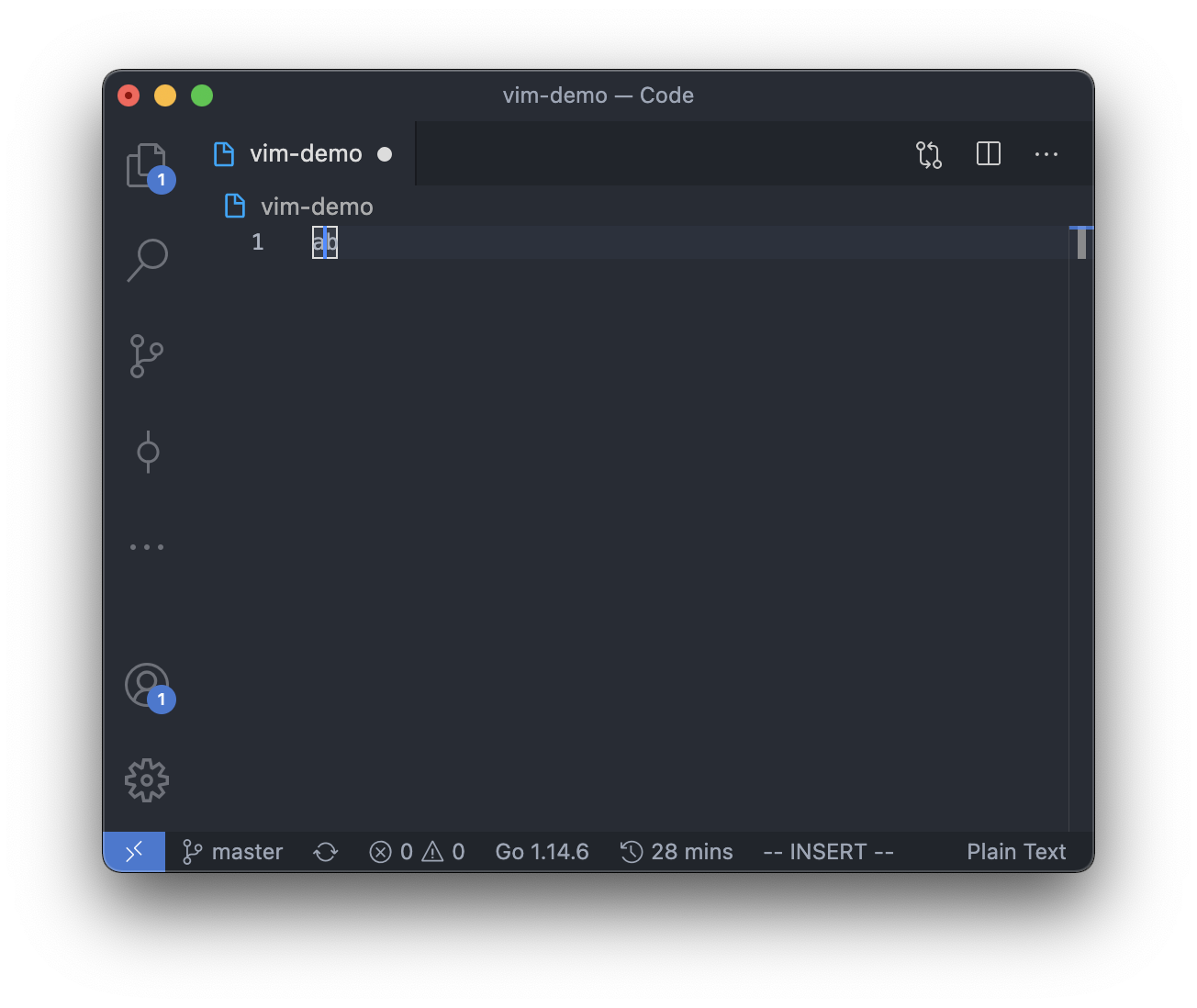
However, in insert mode, the cursor can be between, before or after any of the character,
so there will be 3 possible positions for the cursor in insert mode if the text in the editor is "ab".
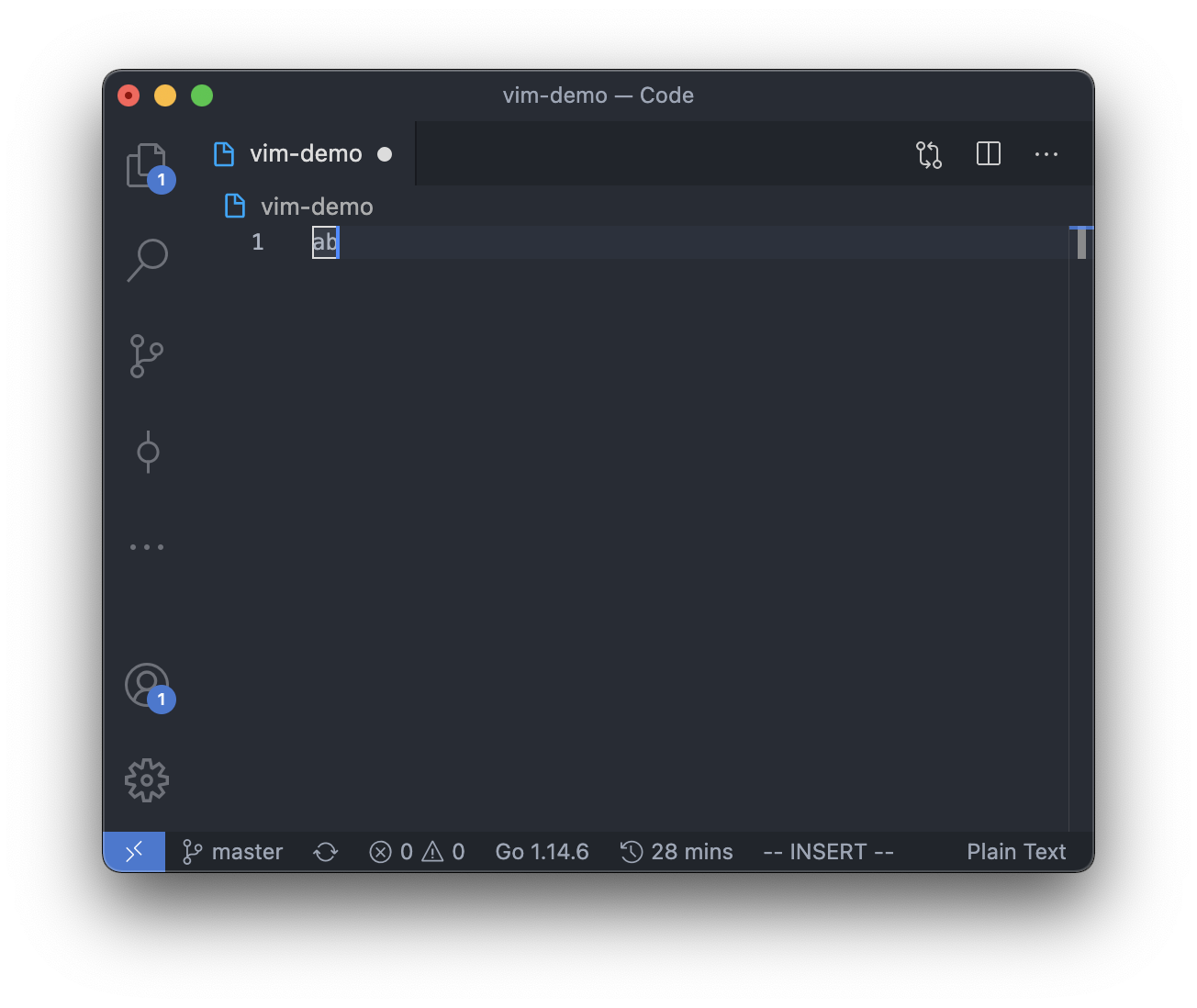
Note that for the difference between command 'a' and 'i':
Note that the cursor posotion from insert mode to normal mode is act as below:
Input
There are multiple test cases.
For each test case, there is only 1 line.
The line contains with a string S, represents the user input.
It is guaranteed that:
- There will be at most 10 test cases in each test file.
- 1 <= |S| <= 200
- In user mode, user only entered lowercase letter
- S always end with ":wq" (without quotes) and only end in command mode
- For command nh, nl and nx, 2 <= n <= 1000
- All input data are valid
Output
For each test case, output the text in the one line Vim editor,
with a newline character at the end.
Note that the answer may be an empty string.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Last Pokemon Contest (神奇寶貝華麗大賽) between Satoshi (小智) and Haruka (小遙) ! After Satoshi won the victory in Battle Pyramid, Satoshi and Haruka signed up for an unofficial Pokemon Contest in Terracotta Town.
Pokemon Contest is a contest in which trainers and Pokemons coordinate strength and beauty. It is divided into two stages. In the first stage, the Performance Stage, trainers and their Pokemons will perform moves to showcase their styles and skills. In the second stage, the Battle Stage, trainers battles against each other as well as demonstrating charm of their Pokemons.
Satoshi and Haruka met in the Battle stage, where Satoshi's Sceptile (蜥蜴王) fought against Haruka's Blaziken (火焰雞). In the final ten seconds of the battle, Haruka's Blaziken activates Blaze (猛火) and fires Overheat (過熱). To battle in a dazzling style, the pattern of Overheat is cleverly designed with golden ratio:

The pattern of Overheat can be expressed with a string. First, Haruka and Blaziken design two short patterns F0 and F1. Then they generate longer patterns using the following recurrence formula: Fn-2 + Fn-1 = Fn (+ means string concatenation). Finally, Haruka tells Blaziken a number n, and Blaziken fires the Overheat with pattern Fn.
Given F0, F1, n, and k, please find out the k-th character in Fn.
For full episode, please google "AG191 Satoshi vs. Haruka! Last Battle!!" or refer to this page.
Explanation on Sample IO
All test data provide same F0 = "abc", F1 = "def". We can generate the following patterns:
-
F2 = "abcdef"
-
F3 = "defabcdef"
-
F4 = "abcdefdefabcdef"
The first test data asks 0-th character of F0, therefore output 'a'. Similarly, the outputs for the second to fifth test data are 'd', 'f', 'f', 'e', respectively.
Input
The input contains multiple test data. The first line of input contains an integer T, being number of test data. After that are T test data.
The first line of test data contains two non-empty strings F0 and F1.
The second line of test data contains two integers n and k.
-
1 <= T <= 100
-
F0 and F1 contain only lower case alphabets (
a-z) and have length no greater than 2000. -
0 <= n < 60 and 0 <= k < |Fn|, where |Fn| is length of Fn
Output
For each test data, output the answer in a single line. Remember to add new line in the end.