| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 11832 | Play cards |
|
| 13129 | prize! |
|
| 13130 | Kuo Wants Prufer Code |
|
| 13137 | binary search tree |
|
Description
Niflheimr is playing cards with his friends. As a CS student, he wants to play in a programmer way. He decides to write a program for shuffling the cards. By the way, more friends may come while he is shuffling cards, so sometimes he needs to insert new cards into the card stack, too.
Hint: You can use linked list to implement.
Input
- ADD idx num: Add a new card with number num before card idx.
- CUT a b: Move cards whose index between a and a+b-1 ( [a, a+b) ) to the top of the card stack. Order of the cards inside the moved part won't be changed.
- 1 ≤ n, m ≤ 104
- Number on cards are non-negative integer and do not exceed 107
- # of cards in the card stack will never exceeds 2*104
- in CUT operation, card with index = a+b-1 always exists.
Output
Print out the card stack from top (index 0) to buttom (largest index), each number occupies one line.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
There are n people, numbered 1 to n, in a circle and arranged in clockwise. They are playing a game, kth lucky people can get the prize.
The following are rules of the game:
1. Each prize has a lucky number.
2. Who count the lucky number can get a prize.
3. If the lucky number is odd, count clockwise.
4. If the lucky number is even, count counterclockwise.
5. The student that gets prize will leave the circle.
6. After someone leave the circle, if the new lucky number is odd, count from the next person, otherwise count from the previous person.
For example:
n = 8
m = 3
lucky number = 3 4 5
The sequence of getting prize is:
1 2 3
2 1 8 7
8 1 2 4 5
Then people 3, 5, 7 can get the prize.
Please use doubly circular linked list to solve this problem.
Input
The first line has two integer n and k, where n is the number of total people, and k is the number of prizes.
The second line has k positive number a1 ~ ak.
testcases:
1. 1 <= k <= n <= 10000, 1 <= ak <= n
2. 1 <= k <= n <= 10000, 1 <= ak <= n
3. 1 <= k <= n <= 10000, 1 <= ak <= n
4. 1 <= k <= n <= 1000000, 1 <= ak <= 10000000, n*k <= 300000000
5. 1 <= k <= n <= 1000000, 1 <= ak <= 10000000, n*k <= 300000000
6. 1 <= k <= n <= 1000000, 1 <= ak <= 10000000, n*k <= 300000000
Output
The output has k lines, each line contains a number: who can get the prize.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Partial Judge Code
13129.cPartial Judge Header
13129.hTags
Discuss
Description
Given a tree with n labeled nodes with labels from 1 to n, a Prufer code uniquely idetifies the tree by the following rule.
At step i, remove the leaf (the nodes with deg = 1) with the smallest label and set the i-th element of the Prüfer sequence to be the label of this leaf's neighbor until only two nodes left.
For example, the Prufer code of the tree below is {4, 4, 4, 5}. (the order of the leaf removed is 1, 2, 3, 4)
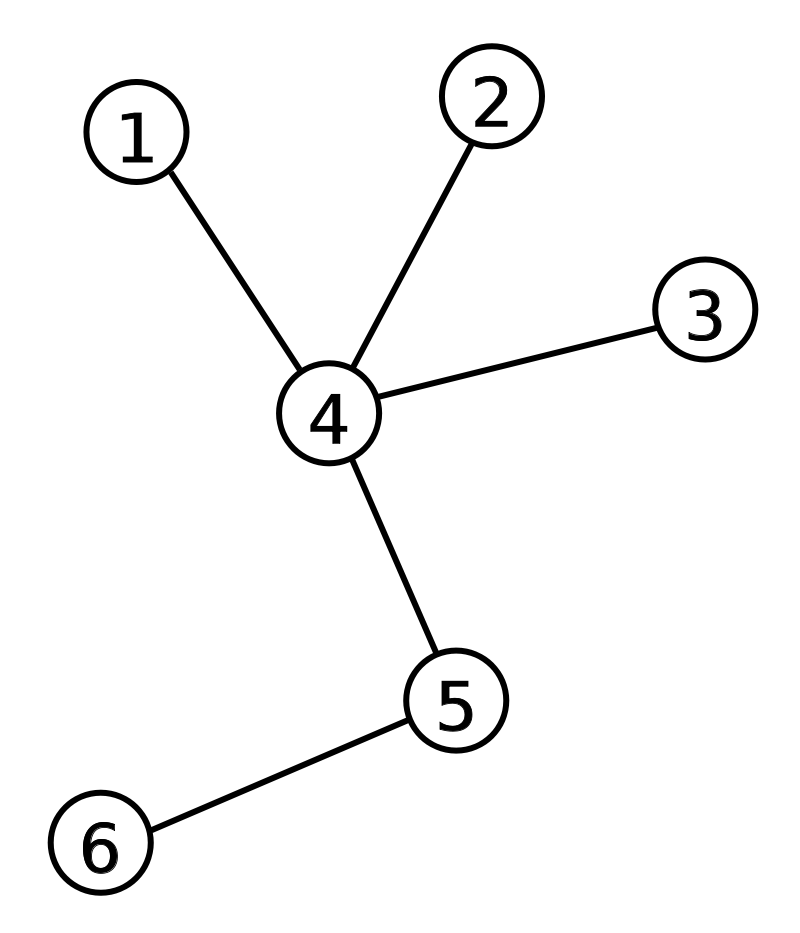
Kuo-chan wants to find the Prufer code of the given trees. Please help him.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n — the number of vertices.
Each of the next n - 1 lines contains two integer vi and ui — meaning there is an edge between vi and ui.
n <= 5000
1 <= vi, ui <= n
Output
The output should contains n - 2 distinct integers, meaning the Prufer code of the tree.
Remember to add new line in the end.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
There's an empty binary search tree, you have to implement two functions:
1. add_node:
- If the tree is empty, the node will be the root node of this tree.
- Otherwise, start to compare with the root node, if the new node is smaller than it, compare with the leftchild, otherwise, compare with the rightchild, until there is no node to compare, place the new node.
- For example:
- There is a binary search tree
- add 7 to this tree
- compare with the root
- 7 >= 5, compare with the rightchild
- 7 < 10, compare with the leftchild
- 7 <= 8 and node 8 has no leftchild, so put 7 to the leftchild of node 8, the tree will be like:
2. showtree: output this tree in in-order
Input
The first line contains a integer n, means how many node to add.
The second line contains n number a1 ~ an, means the value of n node.
testcases:
1. n <= 1000, 0 <= ai <= 109, the sequence of n numbers is increasing.
2. n <= 1000, 0 <= ai <= 109, the sequence of n number is decreasing.
3. n <= 1000, 0 <= ai <= 109.
Output
The output has only one line, contains n numbers, the in-order traversal of binary search tree.
please output a whitespace after every number.