| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 12264 | NPK-easy |
|
| 12306 | beat the monster |
|
| 12817 | Social Distance |
|
| 12819 | 15 Puzzle |
|
| 13239 | Co-Board |
|
Description
Price of fertilizers in the world are raising! Adding Jinkela in fertilizer, one bag can cover two bags!!
People from America, Africa, Japan are lining up in a queue to buy Jinkela. Each person is given a unique id x. The country of each person can be identified by the remainder of his id divided by 3. If x mod 3 = 0, he is from America; if x mod 3 = 1, he is from Africa; if x mod 3=2, he is from Japan. Lining up is tedious, everyone wants to cut in line! These American, African, and Japanese follow some rule when they cut in line:
When a person enters the queue,
- If the queue is empty, he becomes the first person in the queue.
- If there isn't anyone who comes from the same country in the queue, he becomes the last person in the queue.
- Otherwise, of all people coming from the same country in the queue, he finds the last of them and lines up after him ( and possibly cuts in line ).
After a person buys Jinkela, he leaves the queue immediately and will not enter the queue again.
You are curious about the order people get their Jinkela. Given the status of the queue. Whenever someone leaves the queue, output his id.
Refer to the sample IO for example if you don't understand the rule.
For example, assume the queue is empty initially.
- ENQUEUE 0: An American with id 0 enters the queue. Since the queue is empty, he becomes the first person in the queue
queue: 0
- ENQUEUE 1: An African with id 1 enters the queue. Since there isn't any other African in the queue, he becomes the last person in the queue.
queue: 0 1
- ENQUEUE 3: An American with id 3 enters the queue. Since he finds an American (id=0) in the line, he lines up right after him.
queue: 0 3 1
- ENQUEUE 6: An American with id 6 enters the line. He finds two American (id=0, id=3) in the line, where American with id 3 is the last one, he lines up after American with id 3.
queue: 0 3 6 1
- DEQUEUE: The first person leaves the line. Output his id(0).
queue: 3 6 1 output: 0
Input
The status of queue is represented as several commands.
The first line of Input consists of a single integer n (n ≦ 10^6), indicating there are n commands in total.
The following n lines are the commands. There are two kinds of commands:
- ENQUEUE x: person with id x enters the queue. x is an integer, 0 ≦ x ≦ 10^6
- DEQUEUE: the first person in the queue buys his Jinkela and leaves the queue
Output
For each DEQUEUE command, please output the id of person who leaves the queue.
Each output occupies a single line.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
You are playing a game. The goal of this game is to kill the monster when you are still alive (HP > 0, HP = health point). The monster is dead if and only if its HP <= 0.
This game consists of rounds, and you go first in each round.
You have 3 options in each round:
- ATTACK. This will deduct the monster's HP. If your damage point is p, then you can deduct p monster's HP.
- HEAL. You can recover some of your HP, but it can't exceed your max HP.
- Level-up. Level-up might enhance the effect of attacking or healing, but if you are not lucky enough, sometimes it will deduct the effect of attacking and healing. Thus, choosing to level-up is not always a good choice. If you have reached max level, taking this action makes no effect.
In each round, the monster will attack you once with a fixed damage point.
You start the game with full HP and level 1. What is the minimun number of rounds you need to kill the monster?
Input
First line contains 4 numbers L, HP, MHP, MDMG.
- L = max level
- HP = your max HP
- MHP = monster's HP in the beginning of game
- MDMG = monster's damage point
The next L lines describes each level, i-th line of them describes level i. Each of them consists of two numbers, DMG and HL.
- DMG = your damage point when you use ATTACK at level i
- HL = amount of HP you can recover when you use HEAL at level i
Limits:
- L <= 15
- HP <= 300
- MHP <= 400
- MDMG <= 10000
- DMG <= 10000
- HL <= 50
Output
Print a single integer, denoting the mininum number of steps you need to kill the monster.
If you are unable to beat the monster, print -1.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Since we are now undergoing the covid-19 pandemic, the CECC(疫情指揮中心) announce that two people should keep space between themselves at a social distance at s meters.
Inside a classroom, there are n seats numbered from 1 to n in a row and there are walls on the left of the 1-st seat and on the right of the n-th seat. m students numbered from 1 to m are coming to class. The distance between to neighboring seats or walls is 1 meter. Initially there are no people on the seats.

Each student takes a seat and leaves the seat at some time and they will take the seat that is farthest from the wall and the other people. If there are multiple seats to choose from, he or she will choose the leftmost one (i.e. the seat with smallest number).
More detailed description of how a student pick a seat:
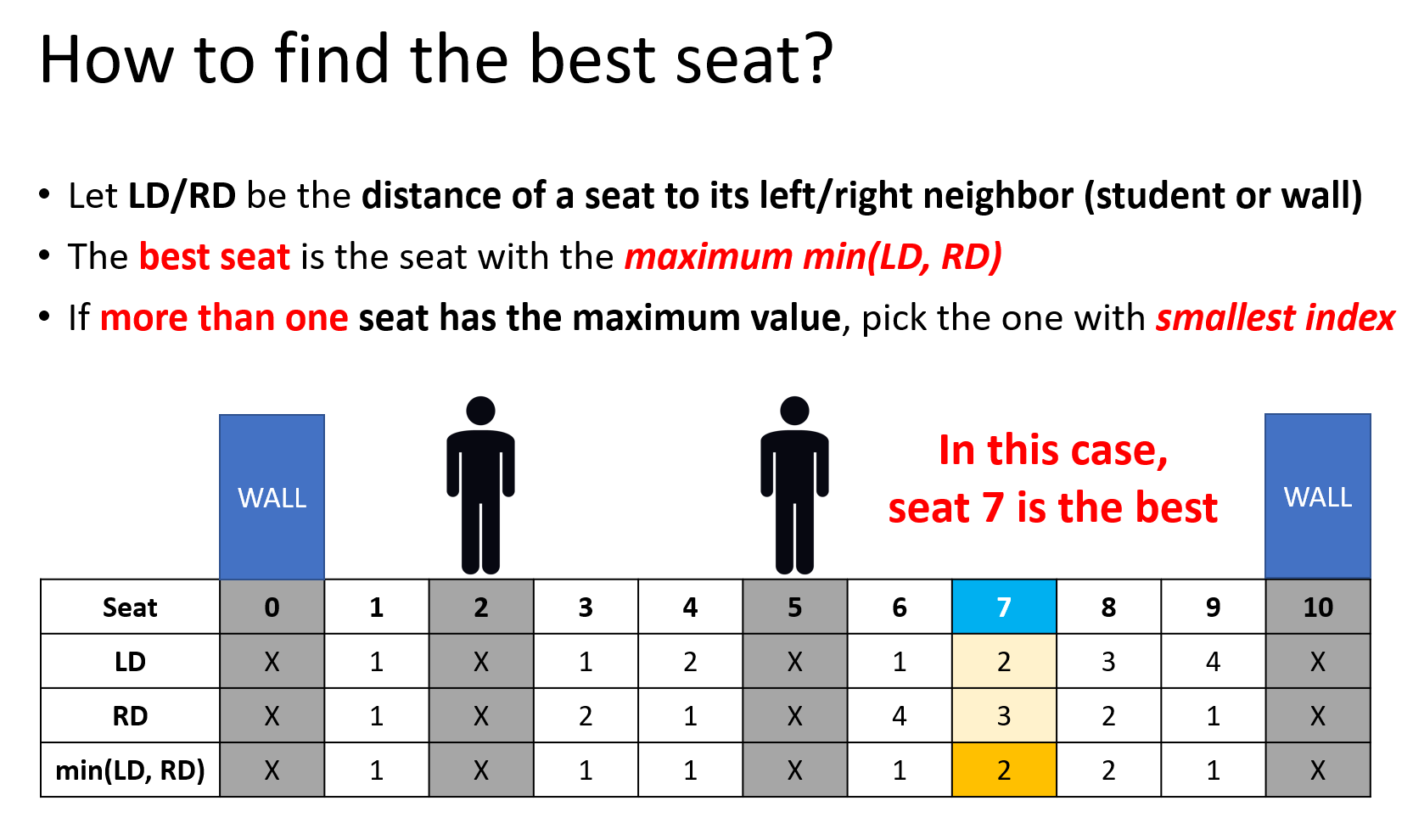
Let D be minimum distance between any two people (note that walls are not people) during the whole class. If D >= s then we say the class is safe, otherwise it is not safe.
Given the time when each student enters and leaves classroom. Your professor wants to know whether he is clockwise whether he follows the CECC's rules , so he wants you to write a program to calculate the value of D and tells him if the class is safe or not.
Explanation for sample IO
Let d be the minimum distance between any two people at a specific time.
-
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _, d = INF -
_ _ _ _ 1 _ _ _ _, d = INF -
_ 2 _ _ 1 _ _ _ _, d = 3 -
_ 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _, d = INF -
_ 2 _ _ _ 3 _ _ _, d = 4 -
_ _ _ _ _ 3 _ _ _, d = INF -
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _, d = INF
During the whole class min d = 3, therefore D = 3 < S = 5, it is not safe.
Input
The first line are three integers n m s (mentioned in problem description).
Then there are 2 x m lines, each line represents the event that one student enters or leaves the classroom. For the k-th line:
-
i xmeans that the student with number x comes in the classroom and takes a seat at time k -
o xmeans that the student with number x leaves the seat and goes out the classroom at time k
It is guaranteed that:
-
A student will never comes back to class after he or she leaves
-
When a student leaves, he or she must be in the classroom (i.e. for a student x,
i xmust appear beforeo x)
Technical Restrictions:
-
For first test case:
-
1 <= m <= n <= 10
-
1 <= s <= 10
-
-
For second test case:
-
1 <= m <= n <= 2000
-
1 <= s <= 2000
-
-
For third test case:
-
1 <= m <= 2000
-
1 <= m <= n, s <= 10^9
-
-
For fourth and fifth test case:
-
1 <= m <= 10^5
-
1 <= m <= n, s <= 10^9
-
Output
Please output D (If D is infinity, then print "INF"). Please output "YES" if it is safe and "NO" if it is not safe.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
The 15-puzzle is a sliding puzzle that consists of a frame of numbered square tiles in random order with one tile missing. The goal of this problem is to transform the arrangement of tiles from the initial arrangement to a goal arrangement.
The legal moves are the moves in which the tiles adjacent to the empty tile are moved to either left, right, up, or down.
Your goal is to find the minimum move to solve the problem.
ouo.
hint
Using BFS/DFS to find answer may exceed memory limit and time limit of some test cases, so we recommend using A* algorithm, which is more efficient. In A* algorithm, it determine the direction of searching by “steps until now + heuristic value”.
A* algorithm: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A*_search_algorithm
To improve heuristic function, you can adopt manhattan distance with Linear Conflict.
Manhattan distance: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taxicab_geometry
Linear Conflict: The tile set(t1, t2) is linear conflict if they have same goal row(column), and they are now in that row(column), but they are blocked by each other. A set of lenear conflict will cause at least two extra steps.
Input
Input contains 4 lines, each line has 4 numbers.
The given puzzle is guaranteed to contain numbers from 0 ~ 15.
The zero denotes the empty tile.
It is guaranteed that the given puzzle is solvable.
Output
Output the minimum move to solve the puzzle.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
A Co-Board consists of 8 integers and they would look like a square. For example, this is a Co-Board:
1 5 3
2 4
7 7 6
And you can execute three types of operations on a Co-Board:
- move all the integers in Co-Board by one-unit in clockwise order
- exchange the position of arbitrary two adjacent integers in Co-Board. For example, in above case, you can exchange the position of 1 and 5. Or you can exchange the position of 3 and 4, etc.
- exchange the position of arbitrary one integer with the integer on its opposite in Co-Board. For example, in above case, you can exchange the position of 1 and 6. Or you can exchange the position of 2 and 4, etc.
Now you are given two Co-Board and
. You need to answer the minimum number of operations you need to execute on
to make
be as same as
. Note it may be impossible to make
be as same as
.
You need to solve tasks.
Input
The first line contains an integer – the number of tasks you need to solve.
The first three line of each task would give the description of . The first and the third line contain three integers. The second line contains two integers. So the description of a Co-Board just look like a Co-Board. The last three line of each task would give the description of
. All the integers in Co-Board must be non-negative and be less than or equal to
.
It's guaranteed that:
- The 1st testcase must be identical to the Sample #1 below
- For the first 4 testcase: only the first type operation is necessary
- For the first 7 testcase: only the first and the second type operations are necessary
Output
For each task, output the minimum number of operations you need to execute on to make
is as same as
.
If it's impossible to make be as same as
, output -1 instead.
Note: there are two sample below. "# Sample Input 1/2" and "# Sample Output 1/2" are not the part of input and output.
They are just for marking that the following content corresponds to which sample.