| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 12264 | NPK-easy |
|
| 13145 | walk on a tree |
|
| 13222 | Sum of Maximum |
|
| 13226 | treasure |
|
| 13227 | Yu-Gi-Oh! |
|
| 13231 | cheat sheet |
|
Description
Price of fertilizers in the world are raising! Adding Jinkela in fertilizer, one bag can cover two bags!!
People from America, Africa, Japan are lining up in a queue to buy Jinkela. Each person is given a unique id x. The country of each person can be identified by the remainder of his id divided by 3. If x mod 3 = 0, he is from America; if x mod 3 = 1, he is from Africa; if x mod 3=2, he is from Japan. Lining up is tedious, everyone wants to cut in line! These American, African, and Japanese follow some rule when they cut in line:
When a person enters the queue,
- If the queue is empty, he becomes the first person in the queue.
- If there isn't anyone who comes from the same country in the queue, he becomes the last person in the queue.
- Otherwise, of all people coming from the same country in the queue, he finds the last of them and lines up after him ( and possibly cuts in line ).
After a person buys Jinkela, he leaves the queue immediately and will not enter the queue again.
You are curious about the order people get their Jinkela. Given the status of the queue. Whenever someone leaves the queue, output his id.
Refer to the sample IO for example if you don't understand the rule.
For example, assume the queue is empty initially.
- ENQUEUE 0: An American with id 0 enters the queue. Since the queue is empty, he becomes the first person in the queue
queue: 0
- ENQUEUE 1: An African with id 1 enters the queue. Since there isn't any other African in the queue, he becomes the last person in the queue.
queue: 0 1
- ENQUEUE 3: An American with id 3 enters the queue. Since he finds an American (id=0) in the line, he lines up right after him.
queue: 0 3 1
- ENQUEUE 6: An American with id 6 enters the line. He finds two American (id=0, id=3) in the line, where American with id 3 is the last one, he lines up after American with id 3.
queue: 0 3 6 1
- DEQUEUE: The first person leaves the line. Output his id(0).
queue: 3 6 1 output: 0
Input
The status of queue is represented as several commands.
The first line of Input consists of a single integer n (n ≦ 10^6), indicating there are n commands in total.
The following n lines are the commands. There are two kinds of commands:
- ENQUEUE x: person with id x enters the queue. x is an integer, 0 ≦ x ≦ 10^6
- DEQUEUE: the first person in the queue buys his Jinkela and leaves the queue
Output
For each DEQUEUE command, please output the id of person who leaves the queue.
Each output occupies a single line.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
You are given a tree of n nodes. Each of the n−1 edges of the tree is given by either '1' or '0'.
Then you need to answer q questions.
Each question has two integers k, m and a sequence of k nodes, a1,a2,…,ak. Let's call a sequence [a1,a2,…,ak] "good" if it satisfies the following criterion:
1. We will walk a path (possibly visiting same edge/node multiple times) on the tree, starting from a1 and ending at ak.
2. Start at a1, then go to a2 using the shortest path between a1 and a2, then go to a3 in a similar way, and so on, until you travel the shortest path between ak−1 and ak.
3. If you walked over at least m '1' edge (marked by '1') during this process, then the sequence is 'good'.
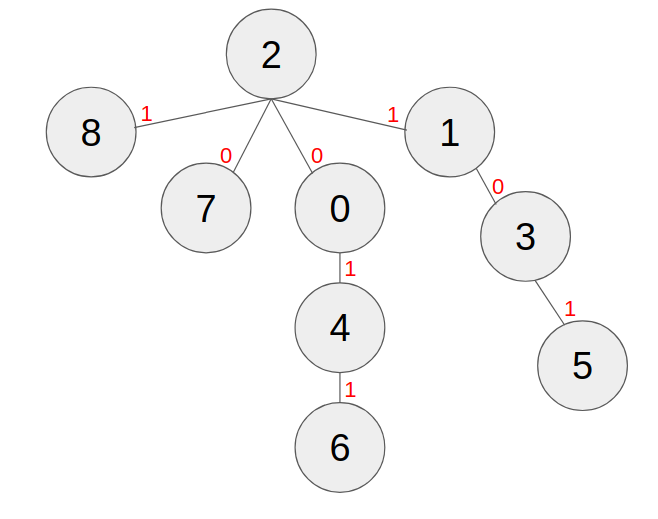
Consider the tree in the above figure. If m = 3, the following sequences are good: [8, 5], [8, 2, 6], [6, 0, 7, 8]. The following sequences are not good: [8, 0, 7], [3, 0, 7, 3], [8, 7, 0, 3].
Hint (You can jump to the Input/Output description first, and come back for hints if necessary):
1. The shortest path is unique.
2. In addition to a linked list, another approch is to use three 2D array to store the tree to save computational time.
- edge[i][j] = 1 means there is an edge between ai and aj.
- path[i][j] means the distance between ai and aj.
- oneedge[i][j] means the number of '1' edge between ai and aj.
3. If there is an edge between ai and ak, and another edge between ak and aj, then the distance between ai and aj is 2, and you can count the number of '1' edge at same time.
Use the tree above as an example:
The edge array will look like:
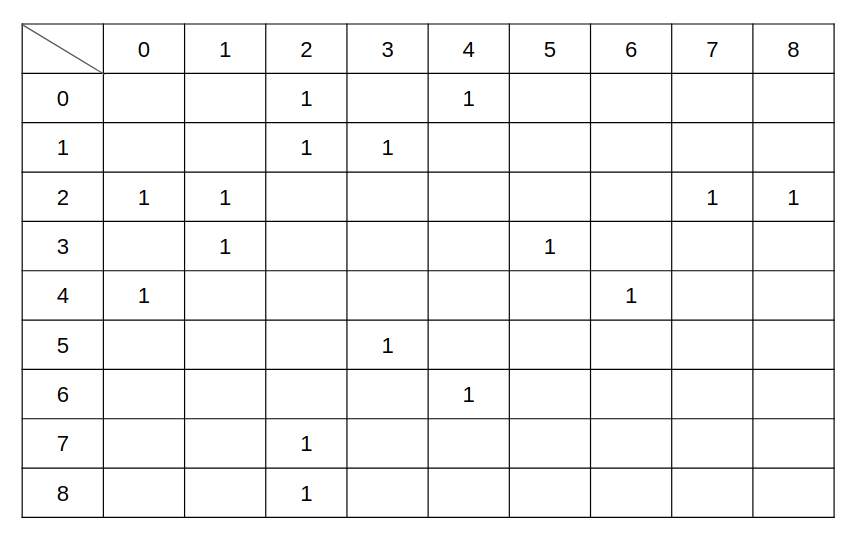
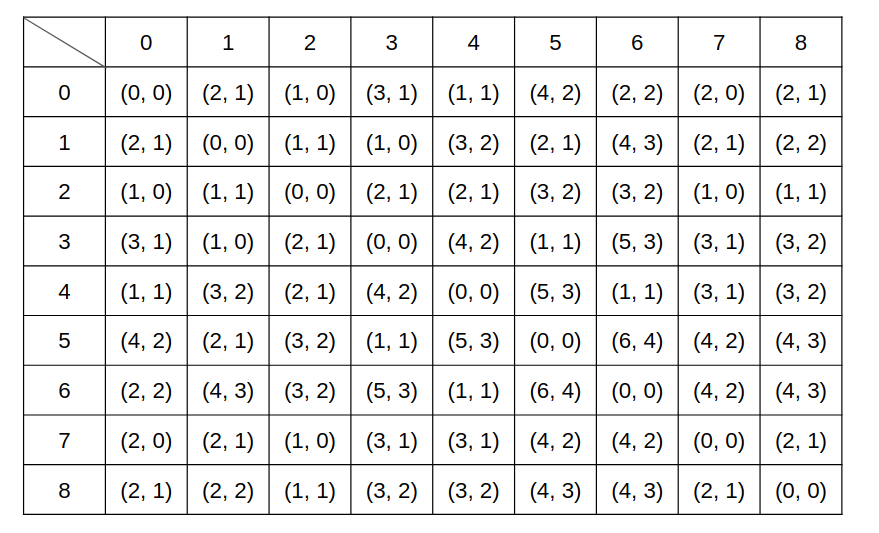
The (path & oneedge array) will look like:
Input
The first line contains two integers n and q, the size of the tree and the number of questions, respectively.
Each of the next n−1 lines contains three integers ui, vi and xi (1 ≤ ui,vi ≤ n, xi ∈ {0,1}), where ui and vi denote the endpoints of the corresponding edge and xi denotes the edge is '0' or '1' .
Each of the next q lines contains k + 2 integers, k, m, and a sequence of k nodes.
testcase:
(1/6) 2 <= n <= 100, 1 <= q <= 100, k = 100, xi = 0
(3/6) 2 <= n <= 100, 1 <= q <= 100, k = 10
(2/6) 2 <= n <= 500, 1 <= q <= 1000, 2 <= k <= 10000
Output
The output has q lines, if the sequence is good, output YES, otherwise output NO.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Given an sequence a1, a2, ..., aN.
Let Max(i, j) be the maximum among ai, ai+1, ..., aj.
Please find the answer to Σi = 1, 2, ...,N Σj = i, i+1, ..., N M(i, j).
For example, if the sequence is 1, 2, 3.
Then M(1, 1) = 1, M(1, 2) = 2, M(1, 3) = 3, M(2, 2) = 2, M(2, 3) = 3, M(3, 3) = 3
Σi = 1, 2, 3 Σj = i, i+1, ..., 3 M(i, j)= M(1, 1) + M(1, 2) + M(1, 3) + M(2, 2) + M(2, 3) + M(3, 3) = 14.
To prevent TLE, add the following code at the first line of your main function and don't use endl in your code.
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer N, the length of the sequence.
The second line contains N numbers a1, a2, ..., aN.
Testcase:
- For testcase 1 and 2, N <= 300.
- For testcase 3 and 4, N <= 5000.
- For testcase 5 and 6, N <= 100000.
- For testcase 7 and 8, N <= 2000000.
Remember to use long long to store the answer.
If you solve this problem by brute force, you can pass the the testcases 1 to 4.
Output
Please output a number as the answer.
Remember to add new line in the end.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
One day, Yayun found a treasure map and started to look for the treasure.
But when she reached the goal marked on the map, there's another treasure map.
When Yayun was confused, an odd man walked over and told her:
"There are k maps in the world, each (ith) map points to the next (i+1th) map. You can find out the treasure locattion if you get the last (kth) map."
Please help Yayun to find the treasure.
Hint: You must find 1st, 2nd, ... k-1th, kth maps in order.
Input
The first line contains a integer k, representing the number of maps you must find.
The second line contains two integer n, m representing the height and width of the map.
The next n lines, each line contains m integers.
- -1: you cannot pass here.
- 0: there is a road here and you can pass.
- 2021: the starting point. You can also pass here agin.
- other integer x: the xth map. You can also pass here.
For all testcases:
(2/6): no -1 on the map, k = 1, 1 <= n, m <= 200
(1/6): k = 1, 1 <= n, m <= 200
(1/6): no -1 on the map, 1 <= k <= 100, 1 <= n, m <= 200
(1/6): 1 <= k <= 100, 1 <= n, m <= 200
(1/6): 1 <= k <= 100, 1 <= n, m <= 200
Output
The minimum steps to find the kth map.
If you cannot find the kth map, output -1.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
Seto Kaiba is a grand master player of Yu-Gi-Oh.
Cards are necessary, and it's why Kaiba buys cards from time to time.
The cards are labeled with numbers.
The card Kaiba has the most is his ace. If there are two or more kinds of cards Kaiba has the most at the same time, the cards with maximum number is Kaiba's ace.
For example,
Buy: 2; Cards in hand: 2; Ace: 2
Buy: 1; Cards in hand: 2 1; Ace: 2 (Becasue 2 is the largest number)
Buy: 1; Cards in hand: 2 1 1; Ace: 1 (Becasue 1 is the most one)
Please find out what Kaiba's ace is whenever he buys a new card.
Input
The first line contains a number N — Kaiba buys N cards in total.
Each of the next N lines contains a number ai — the number of the cards Kaiba buys.
testcase 1 and 2: N <= 100, ai <= 109.
testcase 3 and 4: N <= 3000, ai <= 1018.
testcase 5 and 6: N <= 100000, ai <= 1018.
Output
The output should contains N lines, each of which contains a number — Kaiba's ace.
Remember to add new line at last.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
set:
Sets are containers that store unique elements following a specific order.
#include <set>
begin: Return iterator to beginning
end: Return iterator to end
rbegin: Return reverse iterator to reverse beginning
rend: Return reverse iterator to reverse end
empty: Test whether container is empty
clear: Clear content
size: Return container size
insert: Insert element
erase: Erase elements
find: Get iterator to element
list:
Lists are sequence containers that allow constant time insert and erase operations anywhere within the sequence, and iteration in both directions.
#include <list>
begin: Return iterator to beginning
end: Return iterator to end
rbegin: Return reverse iterator to reverse beginning
rend: Return reverse iterator to reverse end
empty: Test whether container is empty
clear: Clear content
size: Return container size
front: Access first element
back: Access last element
emplace_front: Construct and insert element at beginning
emplace_back: Construct and insert element at the end
push_front: Insert element at beginning
push_back: Insert element at the end
pop_front: Delete first element
pop_back: Delete last element
vector:
Vectors are sequence containers representing arrays that can change in size.
#include <vector>
begin: Return iterator to beginning
end: Return iterator to end
rbegin: Return reverse iterator to reverse beginning
rend: Return reverse iterator to reverse end
empty: Test whether container is empty
clear: Clear content
size: Return container size
front: Access first element
back: Access last element
emplace_back: Construct and insert element at the end
push_back: Add element at the end
pop_back: Delete last element
queue:
#include <queue>
empty: Test whether container is empty
size: Return container size
push: Insert element
pop: remove next element
front: Access next element
stack:
#include <stack>
empty: Test whether container is empty
size: Return container size
top: Access next element
push: Insert element
pop: remove next element
map:
#include <map>
begin: Return iterator to beginning
end: Return iterator to end
rbegin: Return reverse iterator to reverse beginning
rend: Return reverse iterator to reverse end
empty: Test whether container is empty
clear: Clear content
insert: Insert Element
erase: Erase element
count : Count elements with a specific key
find: Get iterator to element
operator[]: Access element
deque:
#include <deque>
push_front: Insert element at beginning
push_back: Insert element at the end
pop_front: Delete first element
pop_back: Delete last element
empty: Test whether container is empty
size: Return container size
insert: Insert element
erase: Erase element
operator []: Access element
front: Access first element
back: Access last element
clear: Clear the container