| # | Problem | Pass Rate (passed user / total user) |
|---|---|---|
| 13348 | DomoMaze - easy version |
|
| 13362 | Gray code |
|
Description

Domo is a brilliant dog. By the way, his grandfather is also a brilliant dog, and he has built a giant maze in the forest years ago, which is called "DomoMaze".
One day, Domo loses his ball called Wilson in this maze. He wants to take Wilson back, and your task is to find out how many ways Domo can reach the position where Wilson is.
This DomoMaze can be described as a two-dimensional array. With width W and length L, Domo is at the position (0, 0) in the beginning, and Wilson is at the position (W-1, L-1).
Each time Domo moves, he can choose one of three ways below:
1. from (i, k) to (i+1, k)
2. from (i, k) to (i, k+1)
3. from (i, k) to (i+1, k+1)
Also, there are some barricades in the maze. You can't enter the barricades on the map.
It is guaranteed that the barricade will not appear at (0, 0) and (W-1, L-1).
Given the size of DomoMaze and the position of all barricades, please find out how many ways Domo can find Wilson.
Input
The first line contains two integers W (1 ≤ W ≤ 15) and L (1 ≤ L ≤ 15) - the width and the length of DomoMaze
For the next W lines, each line has L numbers either 1 or 0 - 0 for empty, and 1 for the barricade.
Output
The output only contains a number and a newline character - the number of ways Domo can reach where Wilson is.
It's guaranteed that the answer will not be greater than 231-1.
Sample Input Download
Sample Output Download
Tags
Discuss
Description
An n-bit gray code sequence is a sequence of 2^n integers where:
- Every integer is in the inclusive range
[0, 2^n - 1], - The first integer is
0, - An integer appears no more than once in the sequence,
- The binary representation of every pair of adjacent integers differs by exactly one bit, and
- The binary representation of the first and last integers differs by exactly one bit.
For example, a if n = 2:
The binary representation of [0,1,3,2] is [00,01,11,10].
- 00 and 01 differ by one bit
- 01 and 11 differ by one bit
- 11 and 10 differ by one bit
- 10 and 00 differ by one bit
Given an integer n, print the gray code sequence.
Note that you have to follow the standard encoding since there are more than one sequences satisfy the requirements.
For example, if n = 4:
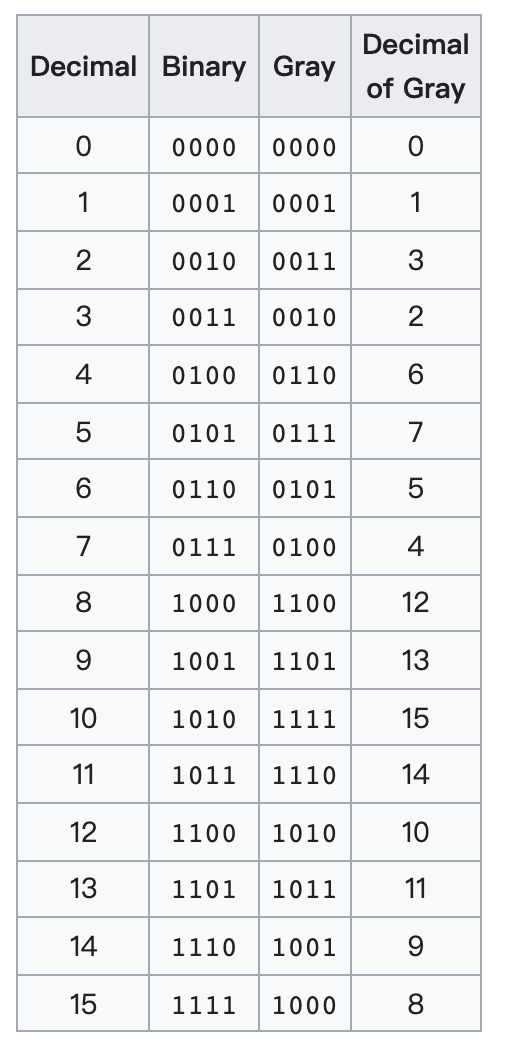
Reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gray_code
Input
1<=n<=20
Output
The corresponding gray code sequence.
Note that you have to print "\n" after each numbers.