Description
A. Definition of Max-Heap
A heap is a complete binary tree.
A max-heap is a complete binary tree in which the value in each internal node is greater
than or equal to the values in the children of that node.
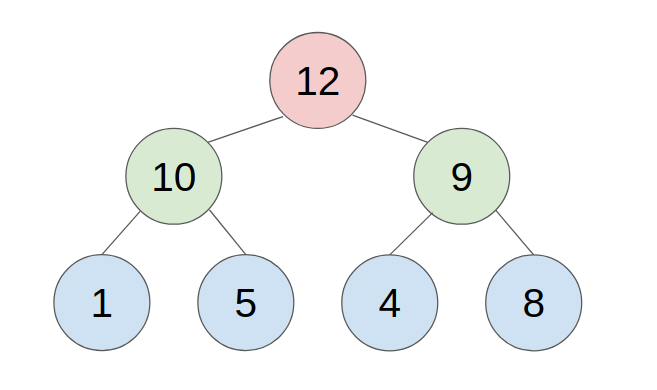
B. Implementation of the Max-Heap Data Structure
1. Array:
An approach to store a max-heap is to use a single, contiguous block of memory cells, i.e., an array, for the entire tree. We store the tree’s root node in the first cell of the array. (Note that, for ease of implementation, we ignore the 0th cell and start from the 1st cell.) Then we store the left child of the root in the second cell, store the right child of the root in the third cell, and in general, continue to store the left and right children of the node found in cell n in the cells 2n and 2n+1 respectively. With this technique, the tree shown below
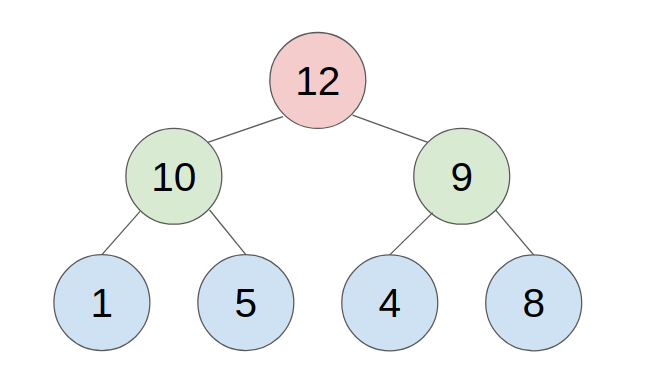
would be stored as follows
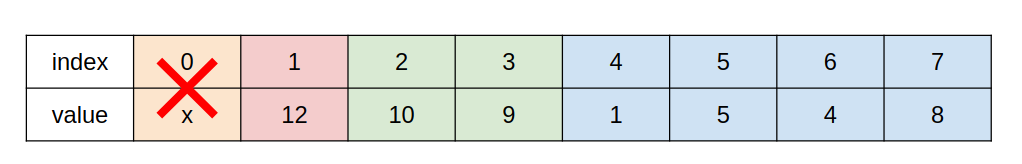
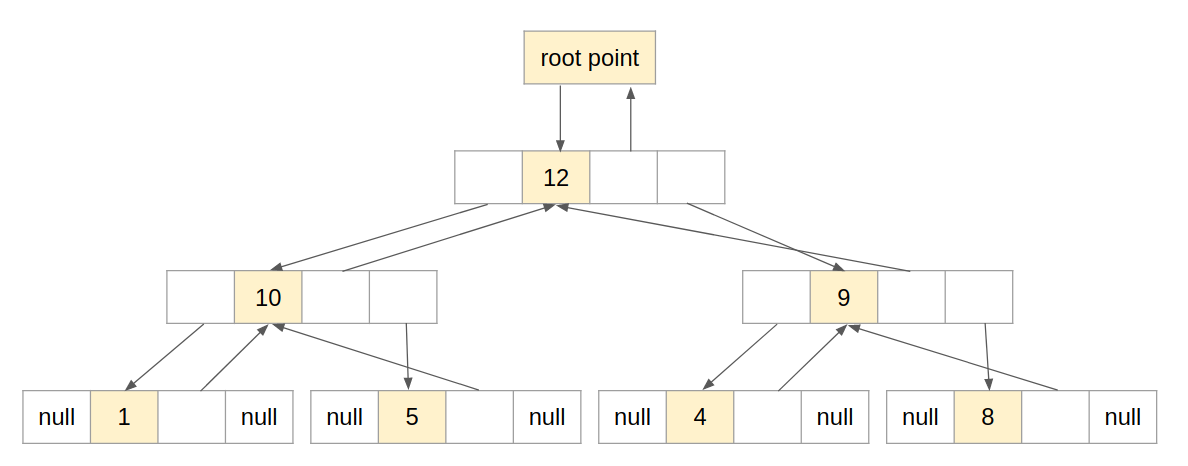
2. Linked list:
We set a special memory location, call a root pointer, where we store the address of the root node. Then each node in the tree must be set to point to the parent and left or right child of the pertinent node or assigned the NULL value if there are no more nodes in that direction of the tree.
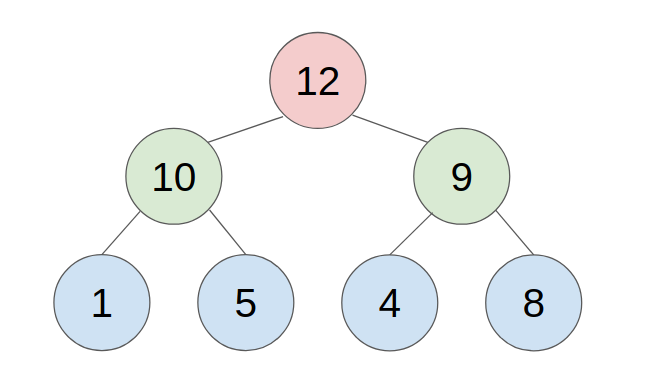
C. Method to push/pop an element
1. PUSH
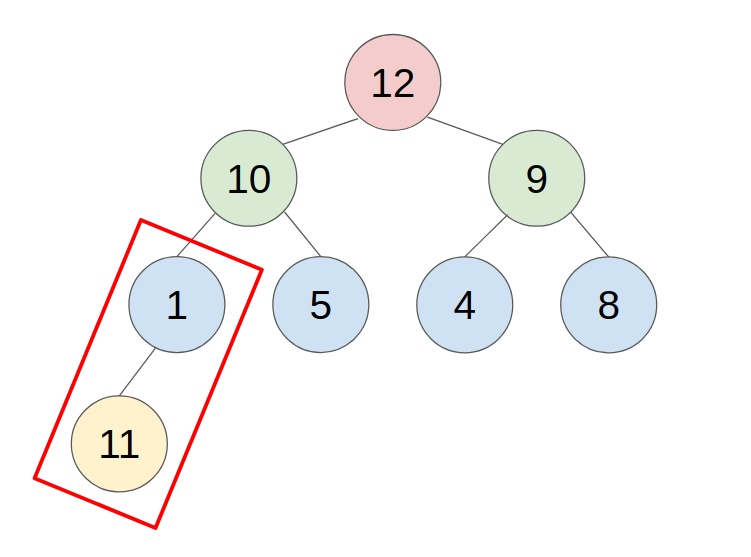
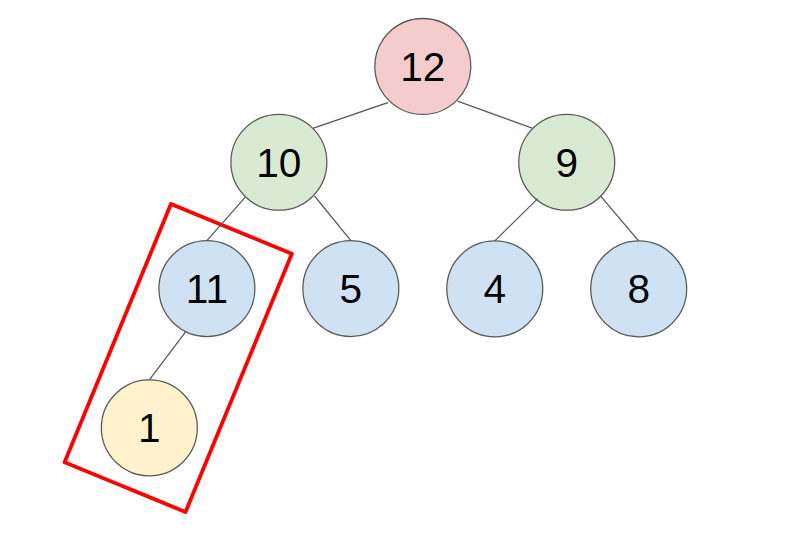
- put the new element in the last place of the heap.
- compare with the parent, swap them until the parent is greater or equal to the new element.
- example: push 11 to this heap
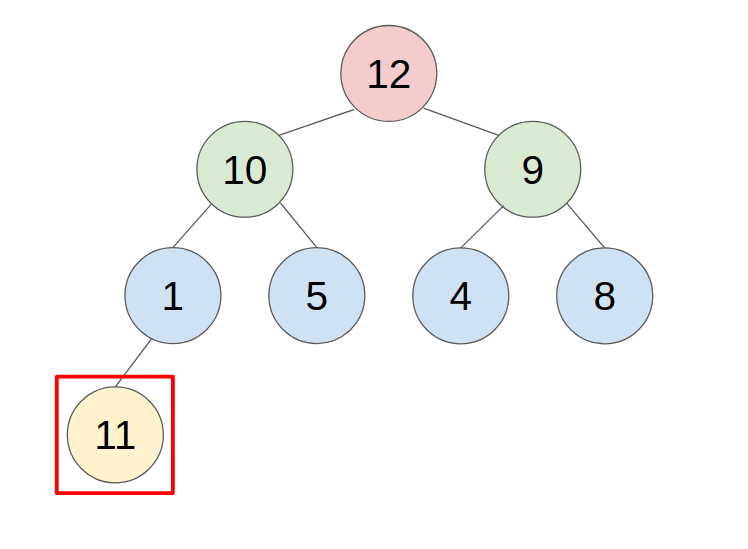
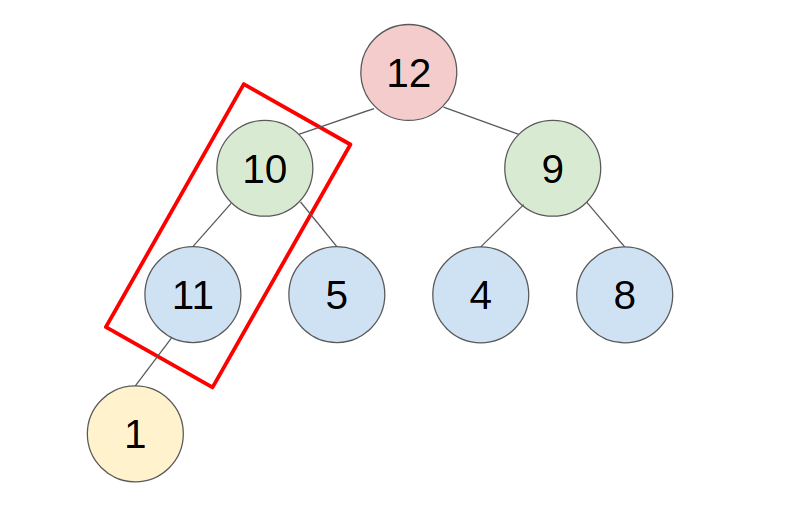
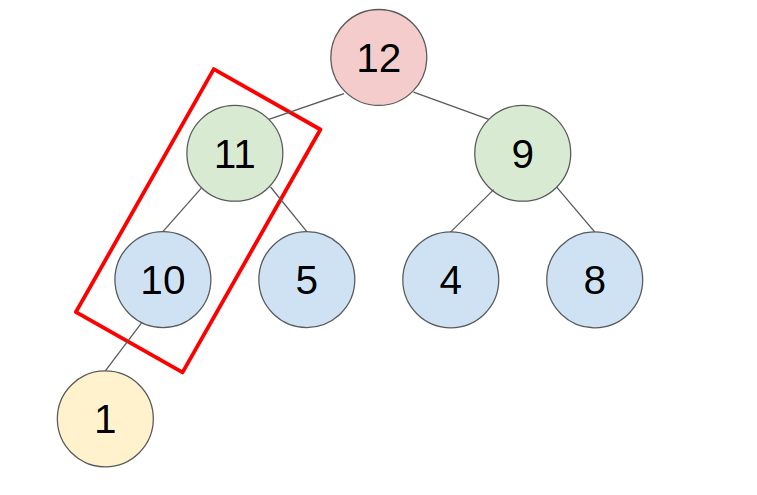
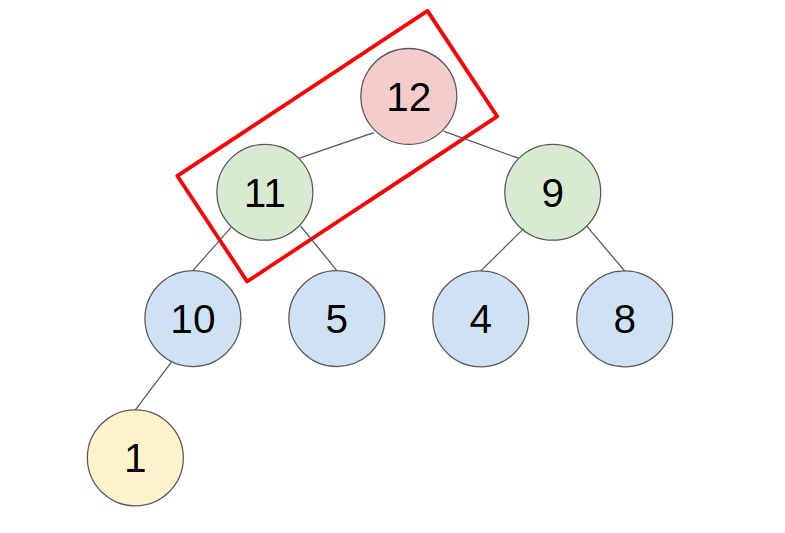
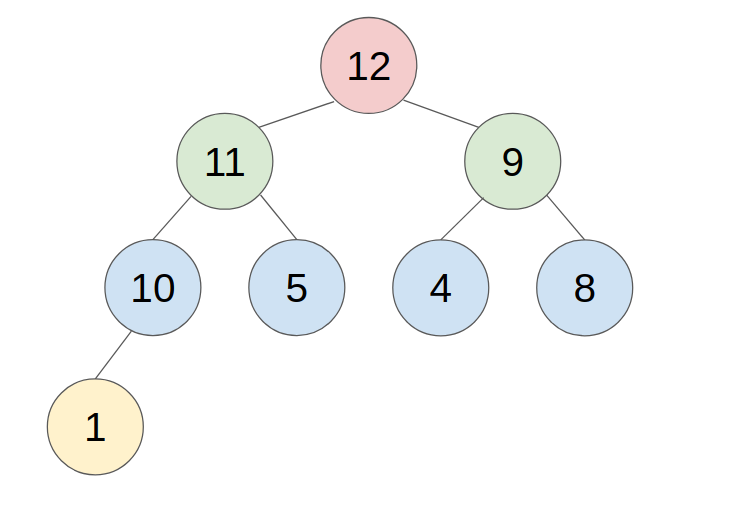
2. POP
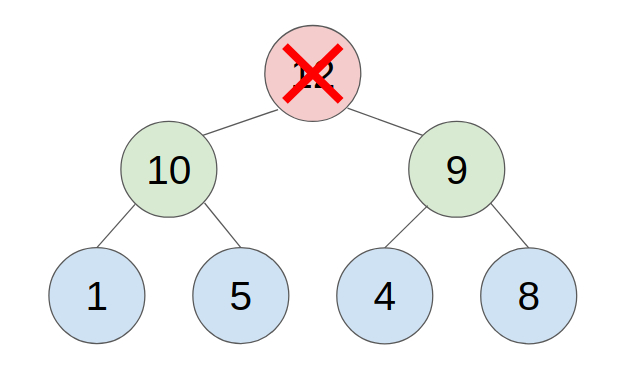
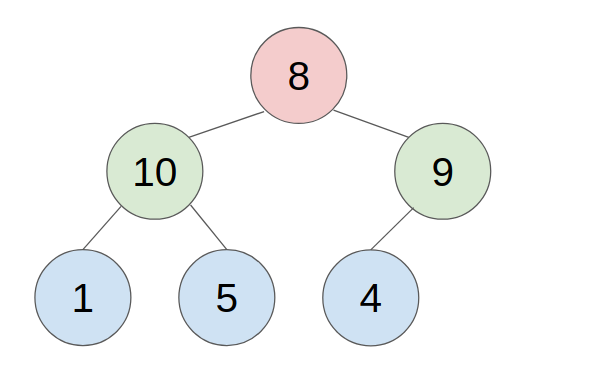
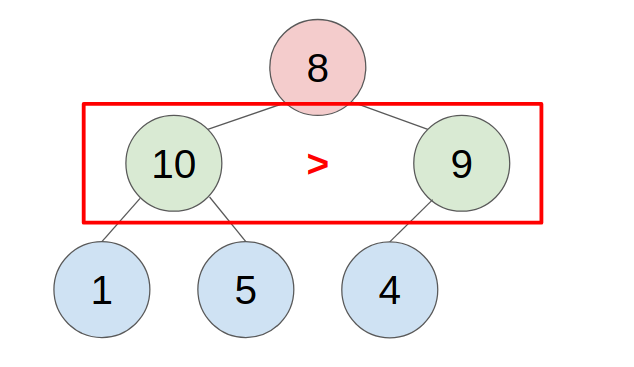
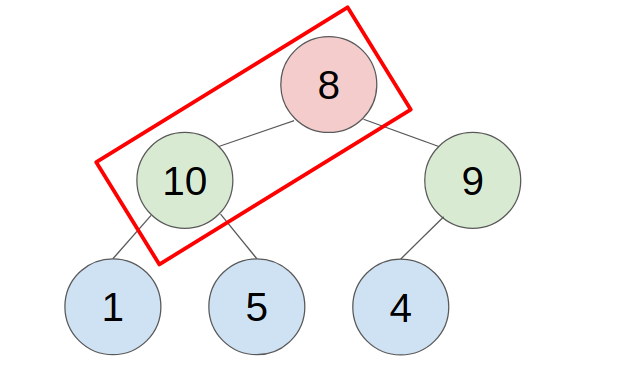
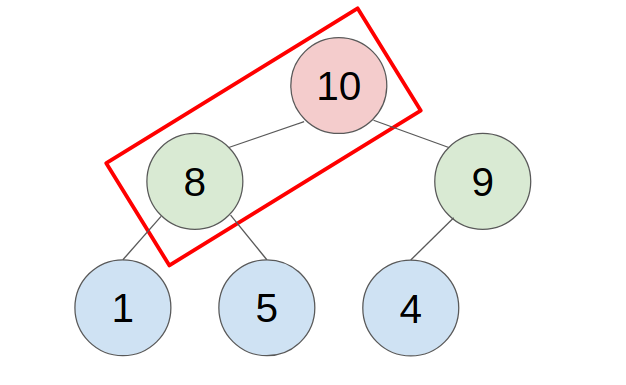
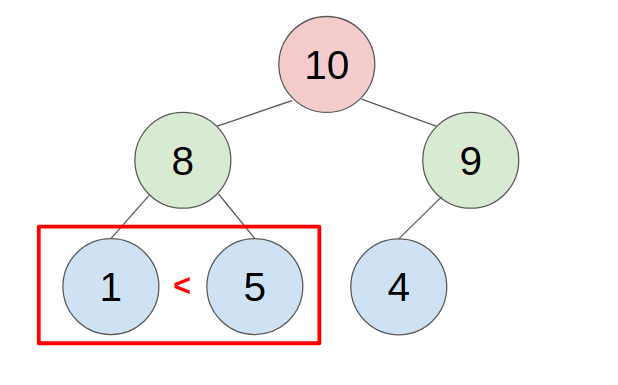
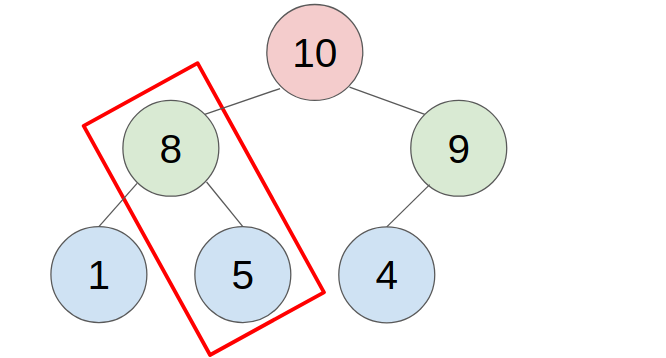
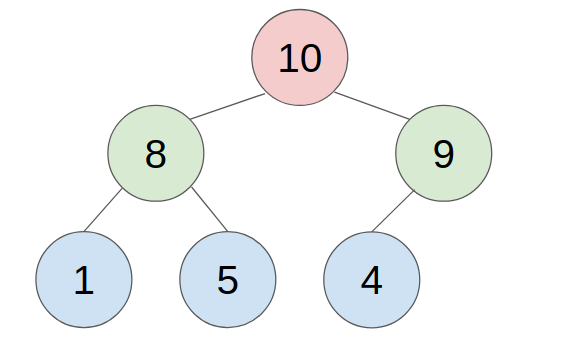
- put the last element to the top(root) of the heap.
- compare with the greater child, swap them until all child is smaller than it.
- example:
REQUIREMENTS:
Implement the constructor, push(), max(), pop() member functions of both the Array_MAX_HEAP and List_MAX_HEAP classes and deleteTree() of List_MAX_HEAP class.
Hint
For easy to solve this problem, you can call findparent(int cnt, ListNode *root) to return a ListNode which is the parent of node[cnt] in List_MAX_HEAP class.
Input
The first line contains an integer n.
Each of the next n lines has an instruction.
The instruction will be either:
- A_push: push a new element ai into the array_max_heap.
- L_push: push a new element ai into the list_max_heap.
- max: show the max element. if the max-heap is empty, print -1.
- A_pop: show and pop the max element in the array_max_heap. if the max-heap is empty, print -1.
- L_pop: show and pop the max element in the list_max_heap. if the max-heap is empty, print -1.
- size: show the size of the heap.
For all testcase:
1 <= n <= 1000, 0 <= ai < 231
(2/6) only A_push, L_push or size instruction
(2/6) only A_push, L_push, size or max instruction
(2/6) contains all instruction
Output
For max, A_pop or L_pop instruction, print the max element in the heap.
For size instruction, print the size of the heap.
Remember to print \n at the end of output.