Description
Today is your birthday, your father wants to prepare a gift for you. He ranks his brains and finally decide what to give. Since you are a college student major in computer science, he gives you a rooted binary tree for your birthday! But at the time you are unpacking the gift, you accidentally damage the binary tree! What a pity! You have tried very hard to restore the information of the binary tree but end up failure. For each node, you know which two nodes are its children, but you don't know which one is left child and which one is right child.
Fortunately, There's an inorder traversal sequence of the binary tree on the package, and you want to know whether the broken information of the binary tree is possible to form the inorder traversal sequence on the package.
Note:
The following figure is the way to form the tree that meets the input of sample testcase 1 and its inorder traversal is identical to the input inorder traversal.
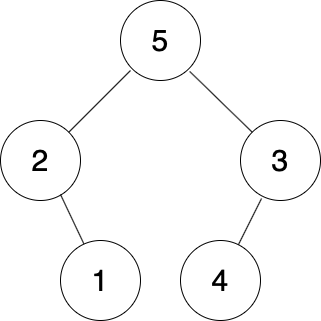
Input
The input contains T testcases.
The first line of each testcase contains a single integer N representing the number of node in the binary tree. The index of nodes in the binary tree is 1-based.
For the following N lines, each line contains two integers. For i-th line, the two integers represent the children of i-th node. 0 represents that the node doesn't exist.
Next line of the input contains N integers representing the inorder traversal sequence.
Constraint of testcases:
Testcase 1: N <= 5, T <= 4.
Testcase 2: T = 20, N <= 15, and node 1 is guarantee to be the root of the binary tree.
Testcase 3: T = 20, N <= 2000, and node 1 is guarantee to be the root of the binary tree.
Testcase 4: N * T <= 4 * 106, N <= 2 * 105, and node 1 is guarantee to be the root of the binary tree.
Testcase 5: T = 20, N <= 15.
Testcase 6: T = 20, N <= 2000.
Testcaes 7: T = 20000, N <= 10.
Testcase 8 ~ 10: N * T <= 4 * 106, N <= 2 * 105.
Output
For each testcase, if there exists a way to distribute nodes to left child or right child that its inorder traversal is identical to the input inorder traversal, then output "YES" otherwise "NO".
Remember to add a newline character at the end of every line.