Description
Today is your birthday, your father wants to prepare a gift for you. He ranks his brains and finally decides what to give. Since you are a college student major in computer science, he gives you a rooted binary tree for your birthday! But at the time you are unpacking the gift, you accidentally damage the binary tree! What a pity! You have tried very hard to restore the information of the binary tree but end up failure. For each node, you know who is its parent. Thus, every node is possible to be at most two nodes' parent. Of course, you don't know which child is left and which child is right.
You spotted that there's an inorder traversal sequence of the binary tree on the package. Unfortunately, it was also damaged while you were unpacking the gift. There are some blanks in the inorder traversal sequence and they have to be filled with arbitrary numbers. You want to know whether the broken information of the binary tree is possible to form the broken inorder traversal sequence on the package.
Note:
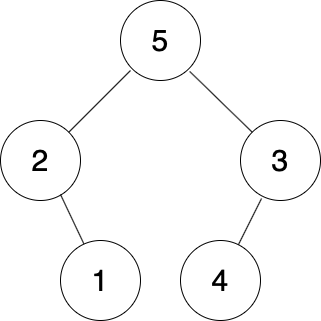
The following figure is the way to form the tree that meets the input of sample testcase 1 and its inorder traversal can match with the non-blank part of the input inorder traversal.
The inorder traversal of the tree is 2 1 5 4 3, it can match with 2 1 _ 4 3.
Input
The input contains T, (T <= 20) testcases.
The first line of each testcase contains a single integer N, (N <= 5000) representing the number of nodes in the binary tree. The indexes of nodes in the binary tree is 1-based.
Next line of the input contains N integers separated by space. The i-th integer represents the parent of node i. 0 represents that the node has no parent.
Next line of the input is the inorder traversal sequence that has K (K <= 6) blanks in it. 0 represents blank. And the values except 0 are pairwise distinct and between 1 ~ N.
Constraint of testcases:
Testcase 1: Identical to sample input.
Testcase 2 ~ 6: K = 0. (The method to solve these testcases is similar to the midterm problem)
Testcaes 7: K = 1.
Testcaes 8: K = 2.
Testcaes 9: K = 3.
Testcase 10: No additional constraint.
Hint:
For all blanks, you can list possible permutations and check whether any of them is correct.
Output
For each testcase, if there exists a way to distribute nodes to left child or right child that its inorder traversal can match with the non-blank part of the input inorder traversal, then output "YES" otherwise "NO".
Remember to add a newline character at the end of every line.