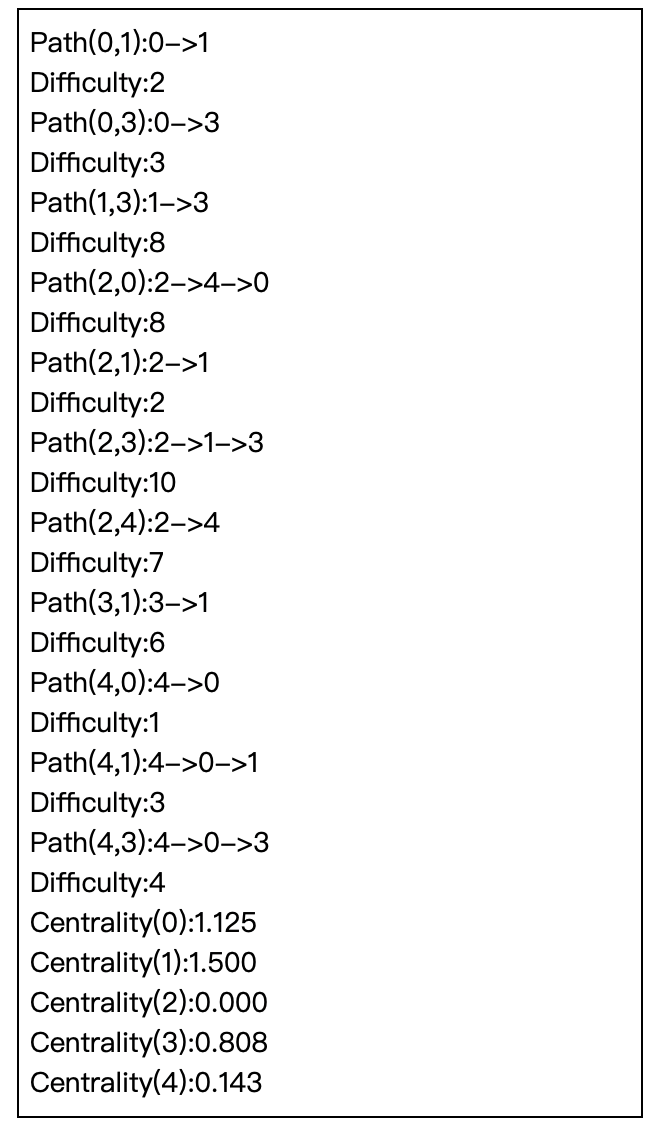
Description
Social network analysis is the process of investigating the structure of a social network. With the analysis, we may benefit users and advertisers in the social network. For example, with the limited budget, advertisers may choose certain users who most probably share the information of products with their friends. The information of products can reach as many people as possible with the limited budget.
In this task, we want to investigate some properties of a social network, where nodes represent users, and directed edges mean that users can propagate information in that direction.
The following graph shows what a social network looks like in this task.
We use the matrix to represent the network.
- Non-zero digits in the matrix represent the weights of the edge between nodes.
- 0 means there are no edges between the nodes.
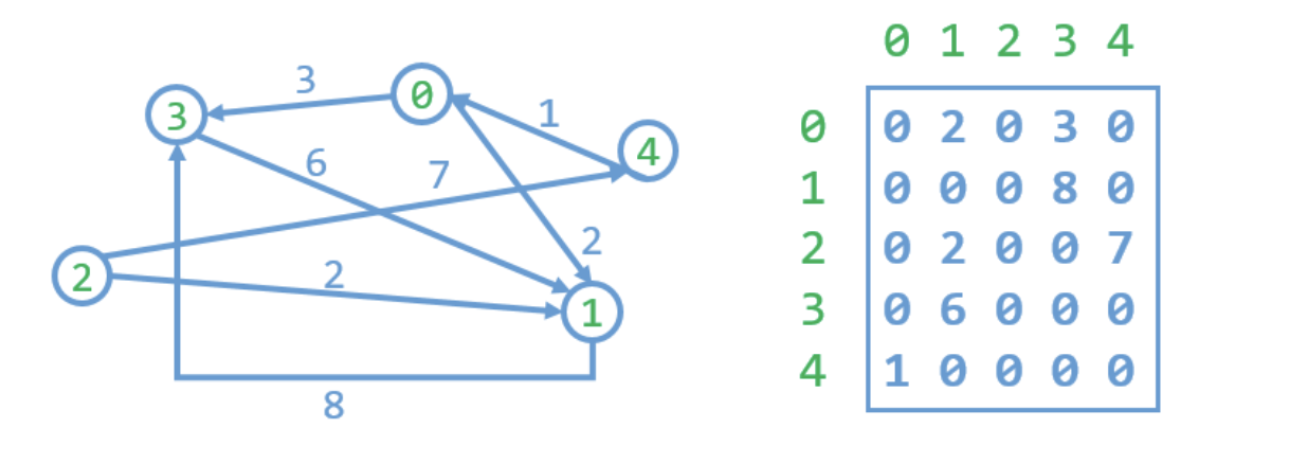
The directed edge from node2 to node1 means node2 can propagate the information to node1.
Node2 can also propagate information to node0 : First propagate the information to node4, and then node4 propagates to node0.
Node1 can not propagate the information to node2 because there are no path from node1 to node2.
The weights of edges represent the difficulty of propagating the information. Smaller difficulty value means that the information is more likely to be propagate.
The difficulty of a propagation path is determined by summing up the difficulty values of edges in the path.
For example, node2 can propagate information to node3 with the propagation path:
2->4->0->3
The difficulty of the path:
7+1+3 = 11
In this task, we want to find out least difficult paths (propagation paths with least difficulty) of each node pair in a given network.
Besides the propagation path, we also want to find out the most important nodes in the network. We use centrality to measure the importance of each node. One of the measurement is harmonic centrality.
The definition of harmonic centrality:
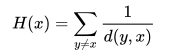
x is the node that we want to know its centrality, while y can be any other nodes in the network. d(y,x) means the difficulty of the least difficult path from y to x in our task. If there are no paths from y to x, 1/d(y,x) is 0.
For example, the least difficult paths to node0 are:
Path(1,0): no path
Path(2,0): 2->4->0 (difficulty = 8)
Path(3,0): no path
Path(4,0): 4->0 (difficulty = 1)
So, the harmonic centrality of node0 is:
0 + 1/8 + 0 + 1 = 0 + 0.125 + 0 + 1 = 1.125
In this task, we also want to find out the harmonic centrality of each node.
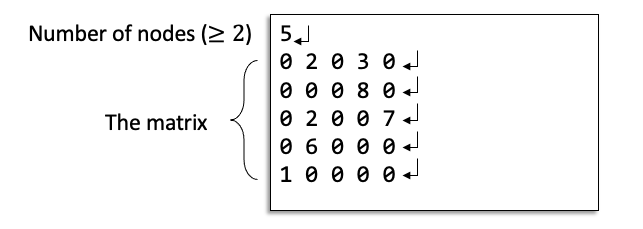
Input
- Given the number of nodes in the social network.
- 2 ≦ Number of nodes ≦ 100
- A matrix contains a digit value
- Non-zero digits represent the weights (difficulty) of the edge between nodes.
- 0 represents no edge between two nodes
- Each digit is between 0 and 9 (0≦digit≦9)
Output
- Print out the least difficult path with row major order and the corresponding difficulty for each pair.
- Path(from,to):from->...->...->to
- Difficulty:xxx
- Print out the harmonic centrality of each node.
- Centrality(node):xxx
- The value of the centrality is accurate to the third digit after the decimal point. You can use iomanip::setprecision(int) to achieve this. Refer to this link for more information.
- You should first sum up the values, and then round the centrality value by using iomanip::setprecision(int).
- If the difficulty of the multiple paths are equivalent, select the one is smaller in string comparison.
- EX: (three paths with the same difficulty)
- path A: 1->2->4->5
- path B: 1->3->4->5
- path C: 1->6->5
- You need to print path A.
- EX:(two paths with the same difficulty)
- path A: 0->10->1
- path B: 0->9->1
- You need to print path A.
- EX:(two paths with the same difficulty)
- path A: 0->1->2
- path B: 0->10->2
- You need to print path A. (ascii of '-' < ascii of '0')
- EX:(two paths with the same difficulty)
- path A: 0->1->3
- path B: 0->3
- You need to print path A.
- EX:(two paths with the same difficulty)
- path A: 2->0
- path B: 2->3->0
- You need to print path A.
- EX:(two paths with the same difficulty)
- path A: 0->1->5->2
- path B: 0->4->3->2
- You need to print path A.
- EX: (three paths with the same difficulty)